Analysis of the Key Elements of Martian Habitable Environment and Its Implication for Tianwen-3 Site Selection
-
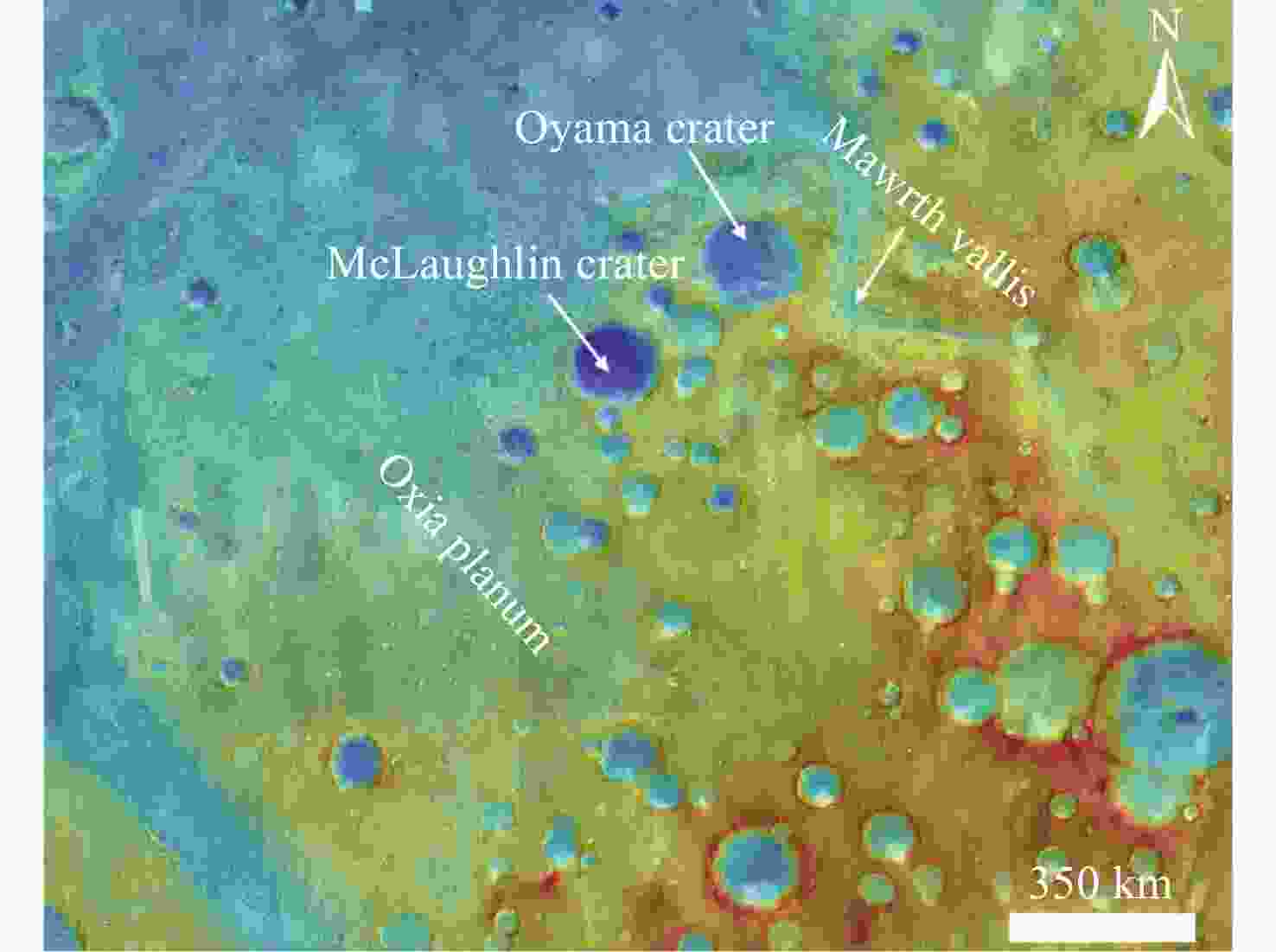
摘要: 火星宜居环境是火星探测和行星科学的重要研究内容之一. 通过分析火星的探测任务及其研究成果, 研究了火星宜居环境的四个关键要素, 包括生命所需关键元素(碳、氮、硫和磷)、液态水、适宜的气候和能量来源. 对比分析乌托邦平原以及阿拉伯高地西北部中的四个典型区域(茅尔斯峡谷、大山撞击坑、麦克劳林撞击坑和奥克夏高原)的地质背景和宜居环境关键要素特征, 结果表明, 乌托邦平原以其广泛的液态水活动痕迹和丰富的生命指示性矿物展现出重要的科学研究价值, 成为天问三号任务的重点候选着陆区. 本研究为天问三号任务着陆区的选择以及火星宜居环境的探索提供了重要的依据.Abstract: The study of Martian habitable environment is an important aspect of Mars exploration and planetary science. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the key factors influencing Martian habitability, by reviewing the research achievements from past Mars exploration missions. The analysis focuses on four essential criteria necessary for life as we know it: the availability of key elements (carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus), the presence of liquid water, suitable climate conditions, and energy sources that could support life. These criteria form the foundation for understanding the potential for life on Mars, both in its past and in possible future scenarios. Based on these factors, comparing and the geological background and key elements of habitable environments of Utopia Planitia and four typical areas of northwest of Arabia Terra (Mawrth Vallis, Oyama Crater, McLaughlin Crater, Oxia Planum). These regions were selected based on their geological characteristics and the available evidence of water-related activity. The findings emphasize that Utopia Planitia, with its extensive traces of ancient liquid water activity, is a promising candidate for landing missions. The region is notable for its rich mineral composition, including the presence of minerals that strongly indicate the past or present potential for habitable conditions. These mineral traces provide invaluable clues regarding the availability of key life-supporting elements and the climatic conditions that could have prevailed in Mars’ ancient past. In contrast, while Mawrth Vallis and Oxia Planum also provide compelling geological evidence of past water activity, they present certain challenges. These regions are known for their complex and highly varied geological history, which makes interpreting the evidence of habitability more difficult. Moreover, the accessibility and preservation of key habitability features in these areas may be compromised due to erosional and environmental factors. On the other hand, Oyama Crater and McLaughlin Crater, although presenting some interesting findings, are less favorable candidates due to their environmental harshness, as well as limited evidence of sustained water activity or suitable conditions for life. The paper reinforces the significance of Utopia Planitia as an important target for future Mars missions, including the Tianwen-3 mission, which aims to explore the planet’s potential for past or present life. And this paper offers critical insights that could guide the selection of landing sites for future missions and advance the exploration of habitable environments on Mars.
-
Key words:
- Mars exploration /
- Habitable environment /
- Landing site /
- Tianwen-3
-
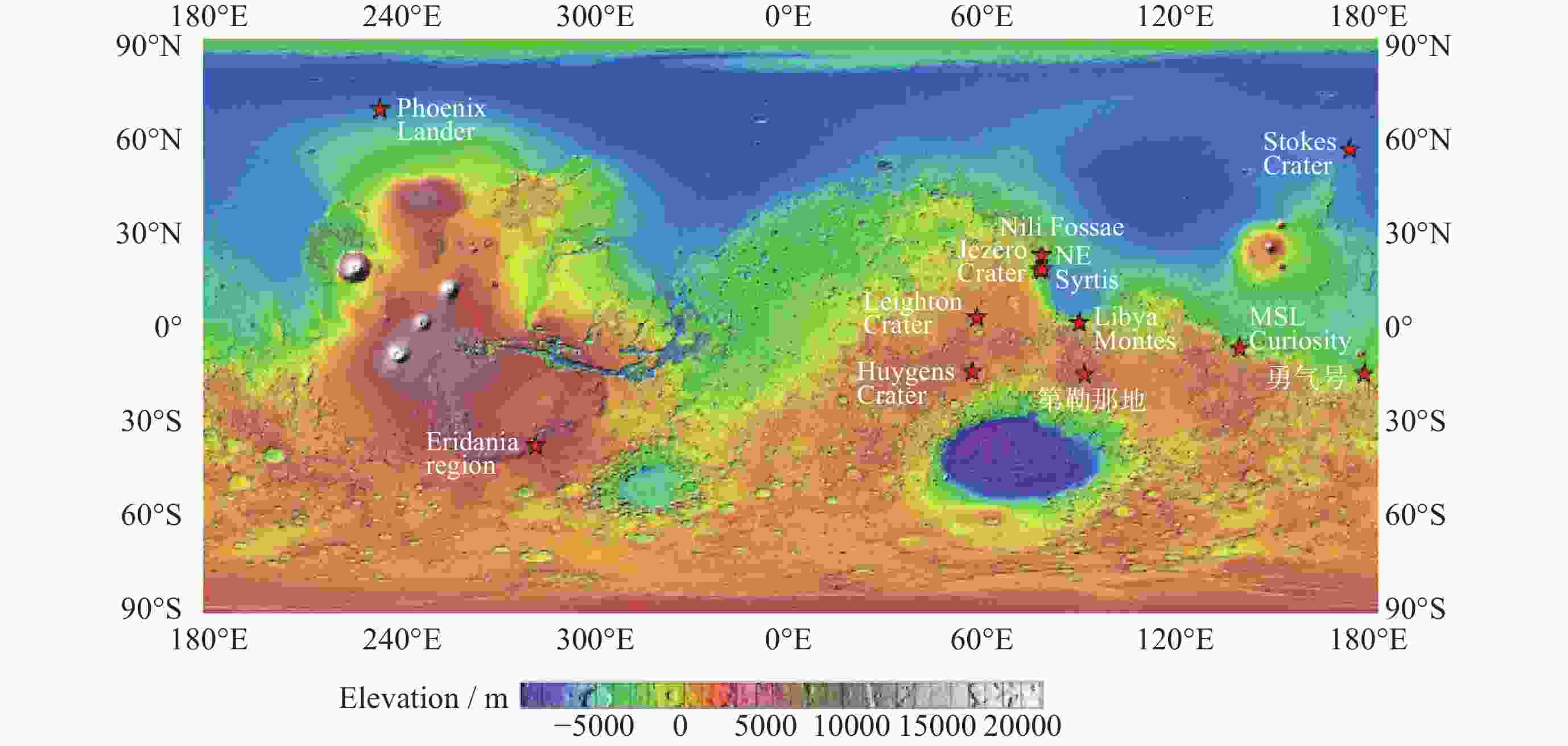
图 2 火星上已在原位(盖尔撞击坑、古谢夫撞击坑、北极)或通过近红外远程观测在8个地点 (特别是古代高地的第勒那地地区)发现碳酸盐地点的MOLA火星激光高度计高程图(红星)(修改自文献 [40])
Figure 2. MOLA map of localities (red stars) on Mars where carbonate has been identified either in situ (Gale crater, Gusev, north pole) or from NIR remote observation at eight localities, particularly around the Tyrrhena Terra region in the Ancient Highlands (Modified from Ref. [40])
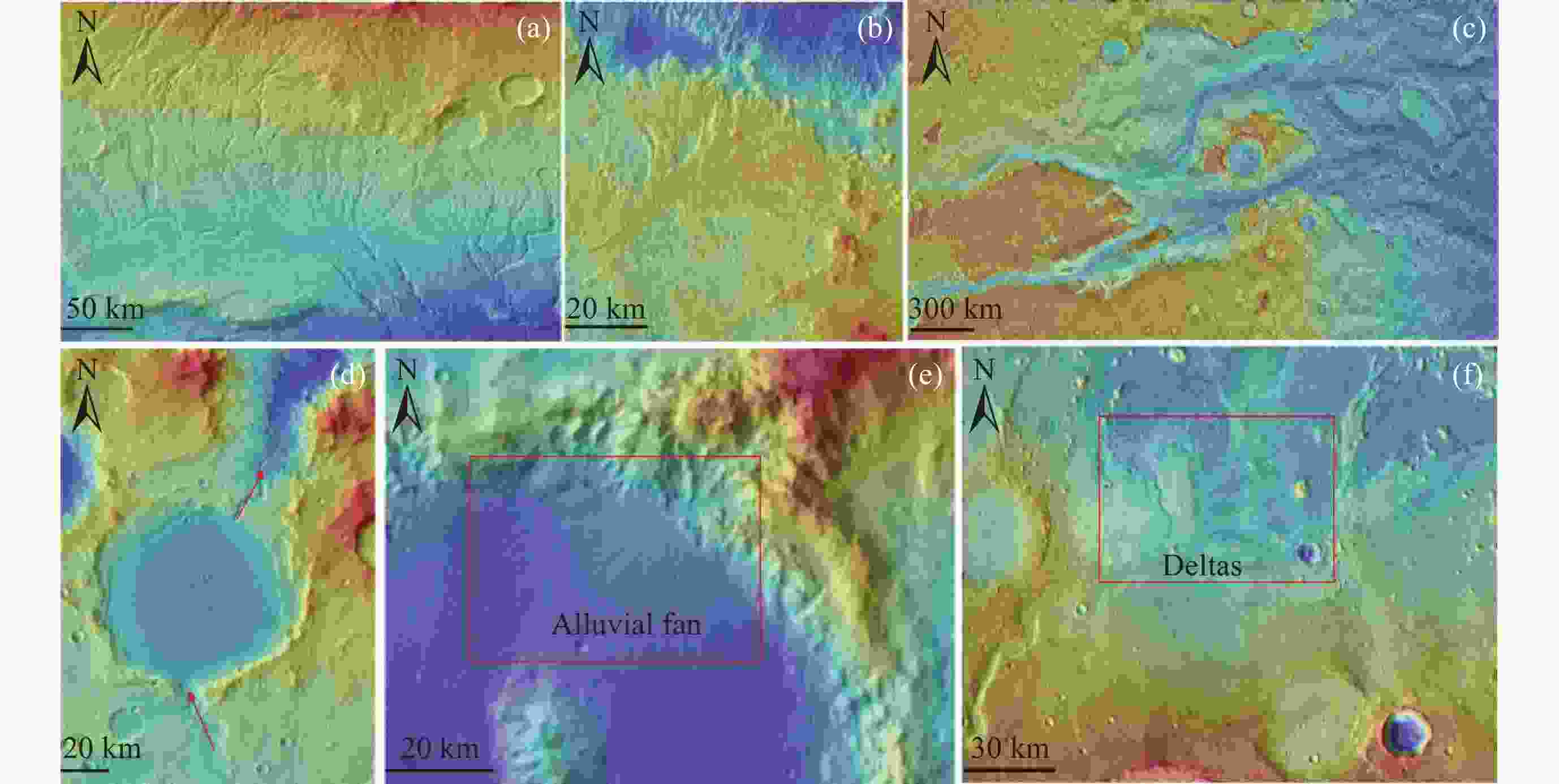
图 5 早期的水流地貌. (a) 网状河谷(中心坐标92.6°W, 42.5°S); (b) 发育在火星扇状沉积上的脊状倒转河道(中心坐标151.4°E, 6.2°S); (c) Kasei谷(中心坐标301.5°E, 27.1°N); (d) 古湖泊(中心坐标174.8°E, 18.6°S), 红色箭头指向水流方向; (e) 冲积扇(中心坐标74.46°E, 22.73°S); (f) 三角洲(中心坐标45°7′28″W, 11°33′21″N). 图像均为MOLA彩色地形图叠加在火星奥德赛热辐射成像系统(THEMIS)日间影像上 (a, b, d, e修改自文献[112]; c修改自文献[115]; f修改自文献[122])
Figure 5. Early fluvial landform. (a) Valley networks (central coordinates 92.6°W, 42.5°S); (b) ridge-like inverted channels developed on Martian fan deposits (central coordinates 151.4°E, 6.2°S); (c) Kasei valles (central coordinates 301.5°E; 27.1°N); (d) Paleolakes (central coordinates 174.8°E, 18.6°S); (e) alluvial fan (central coordinates 74.46°E, 22.73°S); (f) delta (central coordinates 45°7′28″W, 11°33′21″N). The images are MOLA colorized topographic map overlaid on THEMIS mosaics (a, b, d, e are modified from Ref. [112]; c is modified from Ref. [115]; f is modified from Ref. [122])
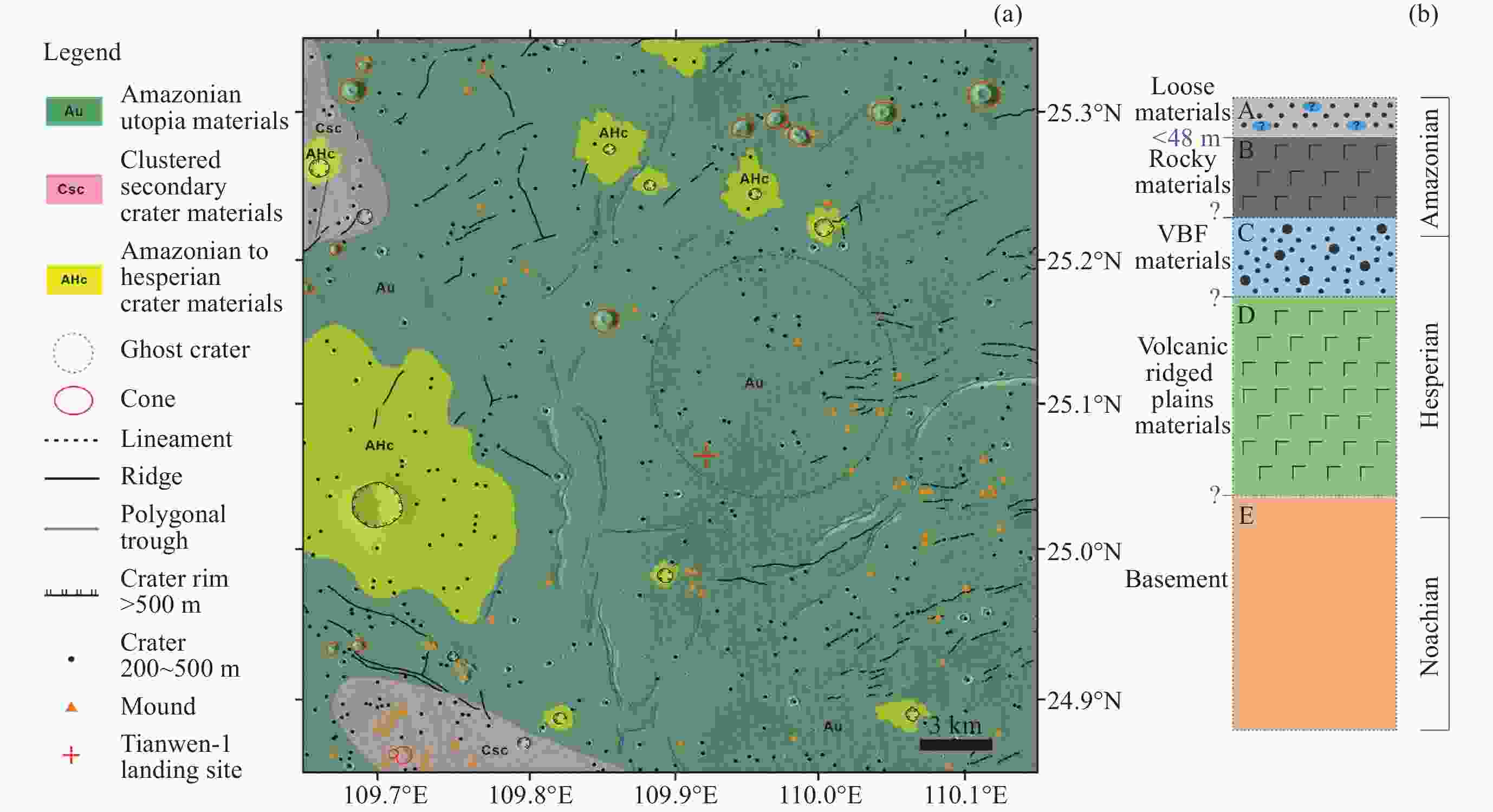
表 1 中国天问三号候选着陆区基于宜居环境关键要素的初步评价
Table 1. Preliminary evaluation of the pre-selected landing zone of China’s Tianwen-3 based on key elements of the habitable environment
地点 中心位置 含水矿物 水环境类型 能量来源 丰富性 茅尔斯峡谷 22.36°N, 343.5°E 高岭石
铁/镁蒙脱石
硫酸盐矿物(黄钾铁矾和石膏)外流河道 热液环境
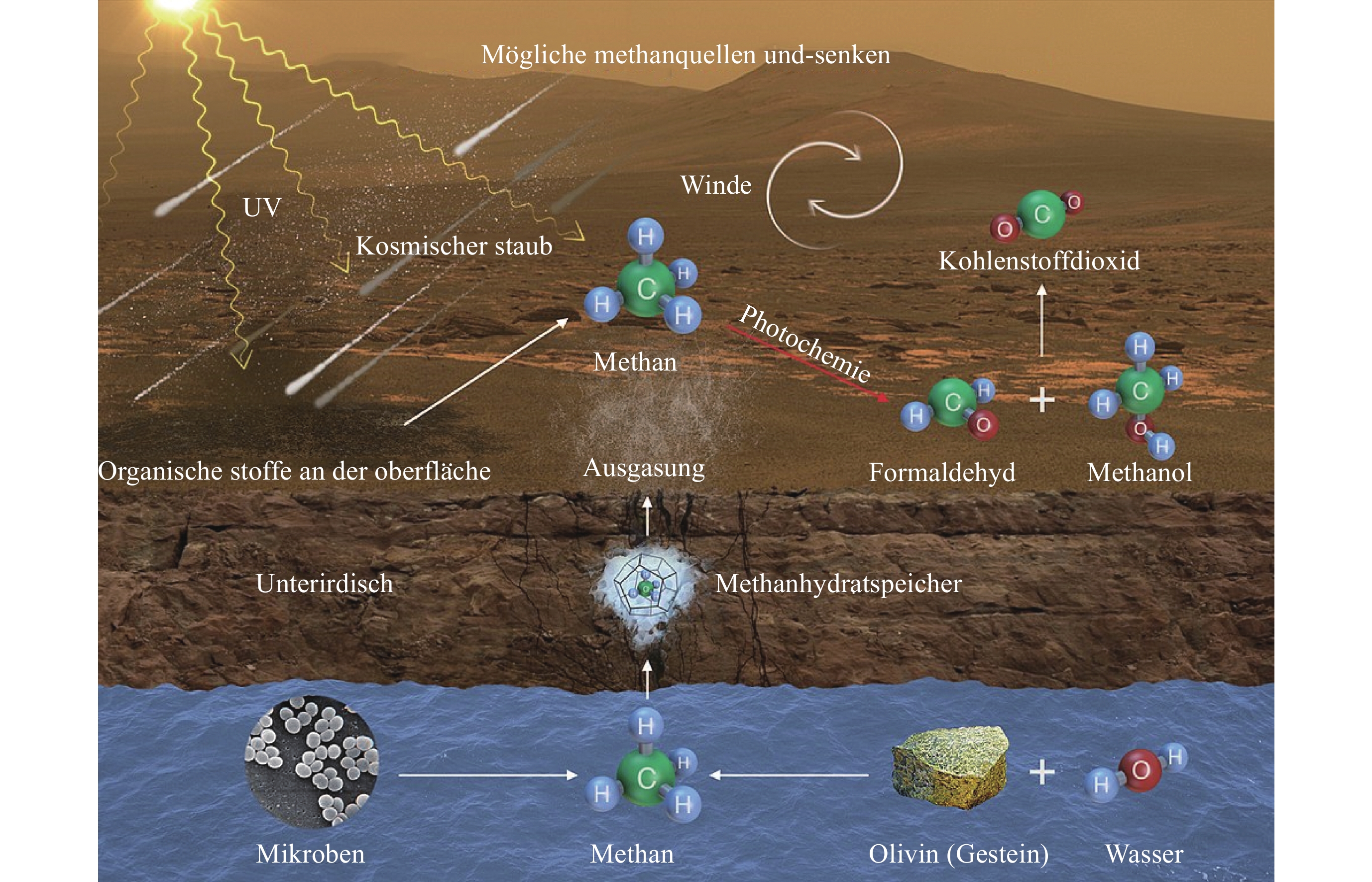
氧化还原诺亚纪
西方纪-亚马逊纪过渡
跨地质年代
有层序信息大山撞击坑 24°N, 340.7°E 铝页硅酸盐
铁/镁蒙皂石河流侵蚀
的倒转地形热液系统 诺亚纪、西方纪
跨地质年代
有层序信息麦克劳林撞击坑 21.9°N, 337.63°E 碳酸盐
镁铁黏土
蛇纹石古湖泊 氧化还原
热液系统诺亚纪
跨地质年代
有层序信息奥克夏高原 18.275°N, 335.368°E 铁、镁黏土矿物 (如绿脱石
和蛭石)
水合二氧化硅古湖泊 氧化还原
热液系统诺亚纪
跨地质年代
有层序信息乌托邦平原 49.7°N, 118°E 含水硫酸盐
碳酸盐
层状硅酸盐古海洋
埋藏河道热液系统 西方纪–亚马逊纪
跨地质年代
有层序信息 -
[1] ARVIDSON R E, GUINNESS E A, MOORE H J, et al. Three Mars years: Viking Lander 1 imaging observations[J]. Science, 1983, 222(4623): 463-468 doi: 10.1126/science.222.4623.463 [2] ARVIDSON R E, GOODING J L, MOORE H J. The Martian surface as imaged, sampled, and analyzed by the Viking landers[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1989, 27(1): 39-60 doi: 10.1029/RG027i001p00039 [3] FOUCHET T, LELLOUCH E, IGNATIEV N I, et al. Martian water vapor: Mars Express PFS/LW observations[J]. Icarus, 2007, 190(1): 32-49 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2007.03.003 [4] LEVIN G V. Odyssey gives evidence for liquid water on Mars[C]//Optical Science and Technology, SPIE’s 48th Annual Meeting. San Diego: SPIE, 2004: 128 [5] ALBEE A L, ARVIDSON R E, PALLUCONI F, et al. Overview of the Mars Global Surveyor mission[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2001, 106(E10): 23291-23316 doi: 10.1029/2000JE001306 [6] NAZARI-SHARABIAN M, AGHABABAEI M, KARAKOUZIAN M, et al. Water on Mars—a literature review[J]. Galaxies, 2020, 8(2): 40 doi: 10.3390/galaxies8020040 [7] VASAVADA A R. Mission overview and scientific contributions from the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover after eight years of surface operations[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2022, 218(3): 14 doi: 10.1007/s11214-022-00882-7 [8] MELLON M T, SIZEMORE H G, HELDMANN J L, et al. The habitability conditions of possible Mars landing sites for life exploration[J]. Icarus, 2024, 408: 115836 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2023.115836 [9] HOEHLER T M, WESTALL F. Mars exploration program analysis group goal one: determine if life ever arose on Mars[J]. Astrobiology, 2010, 10(9): 859-867 doi: 10.1089/ast.2010.0527 [10] PHILLIPS-LANDER C M, AGHA-MOHAMAMDI A, WYNNE J J, et al. Mars Astrobiological Cave and Internal habitability Explorer (MACIE): a new frontiers mission concept[J]. Bulletin of the AAS, 2021, 53(4) [11] FARLEY K A, WILLIFORD K H, STACK K M, et al. Mars 2020 mission overview[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2020, 216(8): 142 doi: 10.1007/s11214-020-00762-y [12] ZHAO Y Y S, YU J, WEI G F, et al. In situ analysis of surface composition and meteorology at the Zhurong landing site on Mars[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(6): nwad056 [13] LI C L, ZHANG R Q, YU D Y, et al. China’s Mars exploration mission and science investigation[J]. Space Science Reviews, 2021, 217(4): 57 doi: 10.1007/s11214-021-00832-9 [14] LI C, ZHENG Y K, WANG X, et al. Layered subsurface in Utopia Basin of Mars revealed by Zhurong rover radar[J]. Nature, 2022, 610(7931): 308-312 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05147-5 [15] XIAO L. Evolution of the geological environment and exploration for life on Mars[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2023, 34(5): 1626-1628 doi: 10.1007/s12583-023-1929-7 [16] XU L, LI H, PEI Z Y, et al. A brief introduction to the international lunar research station program and the interstellar express mission[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2022, 42(4): 511-513 doi: 10.11728/cjss2022.04.yg28 [17] BEATY D W, ALLWOOD A C, VAGO J L, et al. Sedimentology, stratigraphy and astrobiology on Mars in 2018, potentially using two rovers[C]//The First International Conference on Mars Sedimentology and Stratigraphy. El Paso, Texas: Universities Space Research Association, 2010 [18] SCHUUR E A G. Nitrogen from the deep[J]. Nature, 2011, 477(7362): 39-40 doi: 10.1038/477039a [19] ATREYA S K, WITASSE O, CHEVRIER V F, et al. Methane on Mars: current observations, interpretation, and future plans[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2011, 59(2/3): 133-136 [20] SUTTER B, MCADAM A C, MAHAFFY P R, et al. Evolved gas analyses of sedimentary rocks and eolian sediment in Gale Crater, Mars: results of the Curiosity rover’s sample analysis at Mars instrument from Yellowknife Bay to the Namib Dune[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2017, 122(12): 2574-2609 doi: 10.1002/2016JE005225 [21] CHASSEFIÈRE E, LEBLANC F. Methane release and the carbon cycle on Mars[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2011, 59(2/3): 207-217 [22] MUMMA M J, VILLANUEVA G L, NOVAK R E, et al. Strong release of methane on Mars in northern summer 2003[J]. Science, 2009, 323(5917): 1041-1045 doi: 10.1126/science.1165243 [23] BOXE C S, FRANCISCO J S, SHIA R L, et al. New insights into martian atmospheric chemistry[J]. Icarus, 2014, 242: 97-104 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2014.07.023 [24] MCELROY M B, HUNTEN D M. Photochemistry of CO2 in the atmosphere of Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1970, 75(7): 1188-1201 doi: 10.1029/JA075i007p01188 [25] ATREYA S K, GU Z G. Photochemistry and stability of the atmosphere of Mars[J]. Advances in Space Research, 1995, 16(6): 57-68 doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(95)00250-I [26] KORABLEV O, VANDAELE A C, MONTMESSIN F, et al. No detection of methane on Mars from early ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter observations[J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7753): 517-520 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1096-4 [27] FORMISANO V, ATREYA S, ENCRENAZ T, et al. Detection of methane in the atmosphere of Mars[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5702): 1758-1761 doi: 10.1126/science.1101732 [28] NASA/JPL-Caltech. Possible Methane Sources and Sinks [OL]. https://mars.nasa.gov/resources/6891/possible-methane-sources-and-sinks/ (file), Wikipedia: Grafikwerkstatt#Methanhydrat and Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=100873248 [29] WEBSTER C R, MAHAFFY P R, ATREYA S K, et al. Background levels of methane in Mars’ atmosphere show strong seasonal variations[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6393): 1093-1096 doi: 10.1126/science.aaq0131 [30] ATREYA S K, MAHAFFY P R, WONG A S. Methane and related trace species on Mars: origin, loss, implications for life, and habitability[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2007, 55(3): 358-369 doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2006.02.005 [31] OZE C, SHARMA M. Have olivine, will gas: serpentinization and the abiogenic production of methane on Mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(10): L10203 [32] SCHUERGER A C, MOORES J E, CLAUSEN C A, et al. Methane from UV‐irradiated carbonaceous chondrites under simulated Martian conditions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2012, 117(E8): E08007 [33] KEPPLER F, VIGANO I, MCLEOD A, et al. Ultraviolet-radiation-induced methane emissions from meteorites and the Martian atmosphere[J]. Nature, 2012, 486(7401): 93-96 doi: 10.1038/nature11203 [34] KRASNOPOLSKY V A. Some problems related to the origin of methane on Mars[J]. Icarus, 2006, 180(2): 359-367 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2005.10.015 [35] CHASSEFIÈRE E. Metastable methane clathrate particles as a source of methane to the Martian atmosphere[J]. Icarus, 2009, 204(1): 137-144 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.06.016 [36] GOUGH R V, TOLBERT M A, MCKAY C P, et al. Methane adsorption on a Martian soil analog: an abiogenic explanation for methane variability in the Martian atmosphere[J]. Icarus, 2010, 207(1): 165-174 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.11.030 [37] MESLIN P Y, GOUGH R, LEFÈVRE F, et al. Little variability of methane on Mars induced by adsorption in the regolith[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2011, 59(2/3): 247-258 [38] MCMAHON S, PARNELL J, BLAMEY N J F. Sampling methane in basalt on Earth and Mars[J]. International Journal of Astrobiology, 2013, 12(2): 113-122 doi: 10.1017/S1473550412000481 [39] ETIOPE G, OEHLER D Z, ALLEN C C. Methane emissions from Earth’s degassing: implications for Mars[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2011, 59(2/3): 182-195 [40] BRIDGES J C, HICKS L J, TREIMAN A H. Carbonates on Mars[M]//FILIBERTO J, SCHWENZER S P. Volatiles in the Martian Crust. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 89-118 [41] HAUSRATH E M, OLSEN A A. Using the chemical composition of carbonate rocks on Mars as a record of secondary interaction with liquid water[J]. American Mineralogist, 2013, 98(5/6): 897-906 [42] SUTTER B E, HEIL E B, RAMPE R V, et al. Iron-rich carbonates as the potential source of evolved CO2 detected by the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument in Gale Crater[C]//AGU Fall Meeting. Washington D C: AGU, 2015: P31F-07 [43] BOYNTON W V, MING D W, KOUNAVES S P, et al. Evidence for calcium carbonate at the Mars Phoenix landing site[J]. Science, 2009, 325(5936): 61-64 doi: 10.1126/science.1172768 [44] HORGAN B H N, ANDERSON R B, D Geological mapping of Mawrth ROMART G, et al. The mineral diversity of Jezero crater: evidence for possible lacustrine carbonates on Mars[J]. Icarus, 2020, 339: 113526 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2019.113526 [45] SCHELLER E L, SWINDLE C, GROTZINGER J, et al. Formation of magnesium carbonates on earth and implications for Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2021, 126(7): e2021JE006828 doi: 10.1029/2021JE006828 [46] EHLMANN B L, MUSTARD J F, MURCHIE S L, et al. Orbital identification of carbonate-bearing rocks on Mars[J]. Science, 2008, 322(5909): 1828-1832 doi: 10.1126/science.1164759 [47] AMADOR E S, BANDFIELD J L, THOMAS N H. A search for minerals associated with serpentinization across Mars using CRISM spectral data[J]. Icarus, 2018, 311: 113-134 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2018.03.021 [48] JAIN N, CHAUHAN P. Study of phyllosilicates and carbonates from the Capri Chasma region of Valles Marineris on Mars based on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter-Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (MRO-CRISM) observations[J]. Icarus, 2015, 250: 7-17 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2014.11.018 [49] BORG L E, CONNELLY J N, NYQUIST L E, et al. The age of the carbonates in martian meteorite ALH84001[J]. Science, 1999, 286(5437): 90-94 doi: 10.1126/science.286.5437.90 [50] MORRIS R V, RUFF S W, GELLERT R, et al. Identification of carbonate-rich outcrops on Mars by the Spirit Rover[J]. Science, 2010, 329(5990): 421-424 doi: 10.1126/science.1189667 [51] SCHELLER E L, HOLLIS J R, CARDARELLI E L, et al. Aqueous alteration processes in Jezero crater, Mars—implications for organic geochemistry[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6624): 1105-1110 doi: 10.1126/science.abo5204 [52] ANSARI A H. Detection of organic matter on Mars, results from various Mars missions, challenges, and future strategy: a review[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences, 2023, 10: 1075052 doi: 10.3389/fspas.2023.1075052 [53] FREISSINET C, GLAVIN D P, MAHAFFY P R, et al. Organic molecules in the Sheepbed Mudstone, Gale Crater, Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2015, 120(3): 495-514 doi: 10.1002/2014JE004737 [54] KATE I L T. Organic molecules on Mars[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6393): 1068-1069 doi: 10.1126/science.aat2662 [55] MCKAY D S, GIBSON E K, THOMAS-KEPRTA K L, et al. Search for past life on Mars: possible relic biogenic activity in Martian meteorite ALH84001[J]. Science, 1996, 273(5277): 924-930 doi: 10.1126/science.273.5277.924 [56] GIBSON E K, MCKAY D S, THOMAS-KEPRTA K L, et al. Life on Mars: evaluation of the evidence within Martian meteorites ALH84001, Nakhla, and Shergotty[J]. Precambrian Research, 2001, 106(1/2): 15-34 [57] SEPHTON M A, WRIGHT I P, GILMOUR I, et al. High molecular weight organic matter in Martian meteorites[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2002, 50(7/8): 711-716 [58] BRIDGES J C, GRADY M M. Evaporite mineral assemblages in the Nakhlite (Martian) meteorites[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 176(3/4): 267-279 [59] CHANGELA H G, BRIDGES J C. Alteration assemblages in the Nakhlites: variation with depth on Mars[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 2010, 45(12): 1847-1867 [60] LIN Y T, EL GORESY A, HU S, et al. NanoSIMS analysis of organic carbon from the Tissint Martian meteorite: evidence for the past existence of subsurface organic‐bearing fluids on Mars[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 2014, 49(12): 2201-2218 [61] MANCINELLI R L, BANIN A. Where is the nitrogen on Mars?[J]. International Journal of Astrobiology, 2003, 2(3): 217-225 doi: 10.1017/S1473550403001599 [62] NIER A O, MCELROY M B. Composition and structure of Mars’ upper atmosphere: results from the neutral mass spectrometers on Viking 1 and 2[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(28): 4341-4349 doi: 10.1029/JS082i028p04341 [63] MAHAFFY P R, WEBSTER C R, ATREYA S K, et al. Abundance and isotopic composition of gases in the Martian atmosphere from the curiosity rover[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6143): 263-266 doi: 10.1126/science.1237966 [64] EVANS J S, STEVENS M H, LUMPE J D, et al. Retrieval of CO2 and N2 in the Martian thermosphere using dayglow observations by IUVS on MAVEN[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(21): 9040-9049 doi: 10.1002/2015GL065489 [65] LEBLANC F, CHAUFRAY J Y, BERTAUX J L. On Martian nitrogen dayglow emission observed by SPICAM UV spectrograph/Mars Express[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(2): L02206 [66] BOUGHER S W, PAWLOWSKI D, BELL J M, et al. Mars global ionosphere‐thermosphere model: solar cycle, seasonal, and diurnal variations of the Mars upper atmosphere[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2015, 120(2): 311-342 doi: 10.1002/2014JE004715 [67] JAKOSKY B M, GREBOWSKY J M, LUHMANN J G, et al. Initial results from the MAVEN mission to Mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(21): 8791-8802 doi: 10.1002/2015GL065271 [68] MARTI K, KIM J S, THAKUR A N, et al. Signatures of the Martian atmosphere in glass of the Zagami meteorite[J]. Science, 1995, 267(5206): 1981-1984 doi: 10.1126/science.7701319 [69] KOIKE M, NAKADA R, KAJITANI I, et al. In-situ preservation of nitrogen-bearing organics in Noachian Martian carbonates[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1988 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15931-4 [70] MATHEW K J, KIM J S, MARTI K. Martian atmospheric and indigenous components of xenon and nitrogen in the Shergotty, Nakhla, and Chassigny group meteorites[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 1998, 33(4): 655-664 [71] BECKER R H, PEPIN R O. The case for a Martian origin of the shergottites: nitrogen and noble gases in EETA 79001[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 69(2): 225-242 doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90183-3 [72] BECKER R H, PEPIN R O. Nitrogen and light noble gases in Shergotty[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(6): 993-1000 doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90380-7 [73] MIURA Y N, SUGIURA N. Martian atmosphere-like nitrogen in the orthopyroxenite ALH84001[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(3): 559-572 doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00297-5 [74] WRAY J, ARCHER Jr P D, BRINCKERHOFF W B, et al. The search for ammonia in Martian soils with curiosity’s SAM instrument. James[C]//44th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. The Woodlands: Lunar and Planetary Institute, 2013 [75] STERN J C, SUTTER B, FREISSINET C, et al. Evidence for indigenous nitrogen in sedimentary and aeolian deposits from the Curiosity rover investigations at Gale crater, Mars[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(14): 4245-4250 [76] MANNING C V, MCKAY C P, ZAHNLE K J. The nitrogen cycle on Mars: impact decomposition of near-surface nitrates as a source for a nitrogen steady state[J]. Icarus, 2008, 197(1): 60-64 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2008.04.015 [77] GRADY M M, WRIGHT I P, PILLINGER C T. A search for nitrates in Martian meteorites[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 1995, 100(E3): 5449-5455 doi: 10.1029/94JE02803 [78] BADA J L, GLAVIN D P, MCDONALD G D, et al. A search for endogenous amino acids in Martian meteorite ALH84001[J]. Science, 1998, 279(5349): 362-365 doi: 10.1126/science.279.5349.362 [79] MCADAM A C, FRANZ H B, SUTTER B, et al. Sulfur-bearing phases detected by evolved gas analysis of the Rocknest aeolian deposit, Gale Crater, Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2014, 119(2): 373-393 doi: 10.1002/2013JE004518 [80] MCLENNAN S M, BOYNTON W V, KARUNATILLAKE S, et al. Distribution of sulfur on the surface of Mars determined by the 2001 Mars Odyssey gamma ray spectrometer[C]//41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference. The Woodlands: Lunar and Planetary Institute, 2010: 2174 [81] KING P L, MCLENNAN S M. Sulfur on Mars[J]. Elements, 2010, 6(2): 107-112 doi: 10.2113/gselements.6.2.107 [82] GENDRIN A, MANGOLD N, BIBRING J P, et al. Sulfates in Martian layered terrains: the OMEGA/Mars express view[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5715): 1587-1591 doi: 10.1126/science.1109087 [83] MURCHIE S L, MUSTARD J F, EHLMANN B L, et al. A synthesis of Martian aqueous mineralogy after 1 Mars year of observations from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E2): E00D06 [84] MCLENNAN S M, BELL III J F, CALVIN W M, et al. Provenance and diagenesis of the evaporite-bearing Burns formation, Meridiani Planum, Mars[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 240(1): 95-121 doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.09.041 [85] RIEDER R, ECONOMOU T, WÄNKE H, et al. The chemical composition of Martian soil and rocks returned by the mobile alpha proton X-ray spectrometer: preliminary results from the X-ray mode[J]. Science, 1997, 278(5344): 1771-1774 doi: 10.1126/science.278.5344.1771 [86] CLARK B C. Geochemical components in Martian soil[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(19): 4575-4581 doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90183-W [87] CLARK III B C, BAIRD A K, ROSE JR H J, et al. The Viking X ray fluorescence experiment: analytical methods and early results[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(28): 4577-4594 doi: 10.1029/JS082i028p04577 [88] CHRISTENSEN P R, WYATT M B, GLOTCH T D, et al. Mineralogy at Meridiani Planum from the Mini-TES experiment on the opportunity rover[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5702): 1733-1739 doi: 10.1126/science.1104909 [89] KLINGELHÖFER G, MORRIS R V, BERNHARDT B, et al. Jarosite and hematite at Meridiani Planum from Opportunity’s Mössbauer spectrometer[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5702): 1740-1745 doi: 10.1126/science.1104653 [90] SQUYRES S W, KNOLL A H. Sedimentary rocks at Meridiani Planum: origin, diagenesis, and implications for life on Mars[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 240(1): 1-10 doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.09.038 [91] SQUYRES S W, ARVIDSON R E, BELL J F, et al. Ancient impact and aqueous processes at Endeavour Crater, Mars[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6081): 570-576 doi: 10.1126/science.1220476 [92] LANGEVIN Y, POULET F, BIBRING J P, et al. Sulfates in the north polar region of Mars detected by OMEGA/Mars express[J]. Science, 2005, 307(5715): 1584-1586 doi: 10.1126/science.1109091 [93] FRANZ H B, KING P L, GAILLARD F. Sulfur on Mars from the atmosphere to the core[M]//FILIBERTO J, SCHWENZER S P. Volatiles in the Martian Crust. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 119-183 [94] NACHON M, CLEGG S M, MANGOLD N, et al. Calcium sulfate veins characterized by ChemCam/Curiosity at Gale crater, Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2014, 119(9): 1991-2016 doi: 10.1002/2013JE004588 [95] RAO M N, NYQUIST L E, WENTWORTH S J, et al. The nature of Martian fluids based on mobile element studies in salt‐assemblages from Martian meteorites[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2008, 113(E6): 2007JE002958 doi: 10.1029/2007JE002958 [96] FARQUHAR J, KIM S T, MASTERSON A. Implications from sulfur isotopes of the Nakhla meteorite for the origin of sulfate on Mars[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 264(1/2): 1-8 [97] ZHAO Yufen, LIU Yan, HUANG Biling, et al. A potential biomarker phosphate for life exploration on Mars[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(1): 129-132 (赵玉芬, 刘艳, 黄碧玲, 等. 火星生命探测中一种潜在的生物标志物磷酸盐[J]. 空间科学学报, 2021, 41(1): 129-132 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.01.129ZHAO Yufen, LIU Yan, HUANG Biling, et al. A potential biomarker phosphate for life exploration on Mars[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2021, 41(1): 129-132 doi: 10.11728/cjss2021.01.129 [98] HAUSRATH E M, ADCOCK C T, BERGER J A, et al. Phosphates on Mars and their importance as igneous, aqueous, and astrobiological indicators[J]. Minerals, 2024, 14(6): 591 doi: 10.3390/min14060591 [99] ECONOMOU T. Chemical analyses of Martian soil and rocks obtained by the Pathfinder Alpha Proton X-ray spectrometer[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2001, 61(3/4/5/6): 191-197 [100] USUI T, MCSWEEN Jr H Y, CLARK III B C. Petrogenesis of high‐phosphorous Wishstone Class rocks in Gusev Crater, Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2008, 113(E12): E12S44 [101] ADCOCK C T, HAUSRATH E M. Weathering profiles in phosphorus-rich rocks at Gusev Crater, Mars, suggest dissolution of phosphate minerals into potentially habitable near-neutral waters[J]. Astrobiology, 2015, 15(12): 1060-1075 doi: 10.1089/ast.2015.1291 [102] ARVIDSON R E, SQUYRES S W, MORRIS R V, et al. High concentrations of manganese and sulfur in deposits on Murray Ridge, Endeavour Crater, Mars[J]. American Mineralogist, 2016, 101(6): 1389-1405 doi: 10.2138/am-2016-5599 [103] CHAÏRAT C, SCHOTT J, OELKERS E H, et al. Kinetics and mechanism of natural fluorapatite dissolution at 25°C and pH from 3 to 12[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(24): 5901-5912 doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.08.031 [104] BEYSSAC O, FORNI O, COUSIN A, et al. Petrological traverse of the olivine cumulate Séítah formation at Jezero crater, Mars: a perspective from SuperCam onboard perseverance[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2023, 128(7): e2022JE007638 doi: 10.1029/2022JE007638 [105] MCCUBBIN F M, ELARDO S M, SHEARER C K, et al. A petrogenetic model for the comagmatic origin of chassignites and nakhlites: inferences from chlorine‐rich minerals, petrology, and geochemistry[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 2013, 48(5): 819-853 [106] SHEARER C K, BURGER P V, PAPIKE J J, et al. Crystal chemistry of merrillite from Martian meteorites: Mineralogical recorders of magmatic processes and planetary differentiation[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 2015, 50(4): 649-673 [107] LIU Y, MA C, BECKETT J R, et al. Rare-earth-element minerals in Martian breccia meteorites NWA 7034 and 7533: implications for fluid–rock interaction in the Martian crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 451: 251-262 doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2016.06.041 [108] BAZIOTIS I P, LIU Y, DECARLI P S, et al. The Tissint Martian meteorite as evidence for the largest impact excavation[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4(1): 1404 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2414 [109] GU L X, HU S, ANAND M, et al. Occurrence of tuite and ahrensite in Zagami and their significance for shock-histories recorded in Martian meteorites[J]. American Mineralogist, 2022, 107(6): 1018-1029 doi: 10.2138/am-2022-8020 [110] WORDSWORTH R D. The climate of early Mars[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2016, 44(1): 381-408 doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060115-012355 [111] MASURSKY H. An overview of geological results from Mariner 9[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1973, 78(20): 4009-4030 doi: 10.1029/JB078i020p04009 [112] ZHAO Jiannan, SHI Yutong, ZHANG Mingjie, et al. Advances in Martian water-related landforms[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(9): 2755-2768 (赵健楠, 史语桐, 张明杰, 等. 火星水成地貌研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(9): 2755-2768 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.09.009ZHAO Jiannan, SHI Yutong, ZHANG Mingjie, et al. Advances in Martian water-related landforms[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(9): 2755-2768 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.09.009 [113] HYNEK B M, BEACH M, HOKE M R T. Updated global map of Martian valley networks and implications for climate and hydrologic processes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2010, 115(E9): E09008 [114] LIU Yang, LIU Zhenghao, WU Xing, et al. Evolution of water environment on Mars[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(9): 2725-2741 (刘洋, 刘正豪, 吴兴, 等. 火星的水环境演化[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(9): 2725-2741 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.09.007LIU Yang, LIU Zhenghao, WU Xing, et al. Evolution of water environment on Mars[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(9): 2725-2741 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.09.007 [115] LIU Yang, WU Xing, LIU Zhenghao, et al. Geological evolution and habitable environment of Mars: progress and prospects[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2021, 52(4): 416-436 (刘洋, 吴兴, 刘正豪, 等. 火星的地质演化和宜居环境研究进展[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 2021, 52(4): 416-436LIU Yang, WU Xing, LIU Zhenghao, et al. Geological evolution and habitable environment of Mars: progress and prospects[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 2021, 52(4): 416-436 [116] VIJAYAN S, SINHA R K. Amazonian fluvial outflow channels in Jovis Tholus region, Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2017, 122(5): 927-949 doi: 10.1002/2016JE005237 [117] GALLAGHER C J, BAHIA R. Outflow channels on Mars[M]//SOARE R J, CONWAY S J, WILLIAMS J P, et al. Mars Geological Enigmas. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2021: 13-40 [118] LEONE G. Mangala Valles, Mars: a reassessment of formation processes based on a new geomorphological and stratigraphic analysis of the geological units[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2017, 337: 62-80 doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2017.03.011 [119] HARRISON K P, GRIMM R E. Multiple flooding events in Martian outflow channels[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2008, 113(E2): E02002 [120] HOVIUS N, LEA-COX A, TUROWSKI J M. Recent volcano–ice interaction and outburst flooding in a Mars polar cap re-entrant[J]. Icarus, 2008, 197(1): 24-38 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2008.04.020 [121] CABROL N A, GRIN E A. Distribution, classification, and ages of Martian impact crater lakes[J]. Icarus, 1999, 142(1): 160-172 doi: 10.1006/icar.1999.6191 [122] WANG L, HUANG J. Hypothesis of an ancient northern ocean on Mars and insights from the Zhurong rover[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2024, 8(10): 1220-1229 doi: 10.1038/s41550-024-02343-3 [123] FASSETT C I, HEAD III J W. Fluvial sedimentary deposits on Mars: ancient deltas in a crater lake in the Nili Fossae region[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(14): L14201 [124] WILSON S A, MORGAN A M, HOWARD A D, et al. The global distribution of craters with alluvial fans and deltas on Mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(4): e2020GL091653 doi: 10.1029/2020GL091653 [125] PASQUON K, GARGANI J, MASSÉ M, et al. Present-day formation and seasonal evolution of linear dune gullies on Mars[J]. Icarus, 2016, 274: 195-210 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2016.03.024 [126] DUNDAS C M, DINIEGA S, MCEWEN A S. Long-term monitoring of Martian gully formation and evolution with MRO/HiRISE[J]. Icarus, 2015, 251: 244-263 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2014.05.013 [127] DUNDAS C M, MCEWEN A S, DINIEGA S, et al. New and recent gully activity on Mars as seen by HiRISE[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(7): L07202 [128] HEAD J W, MARCHANT D R, KRESLAVSKY M A. Formation of gullies on Mars: link to recent climate history and insolation microenvironments implicate surface water flow origin[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(36): 13258-13263 [129] HARRISON T N, OSINSKI G R, TORNABENE L L, et al. Global documentation of gullies with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Context Camera and implications for their formation[J]. Icarus, 2015, 252: 236-254 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2015.01.022 [130] PARKER T J, SAUNDERS R S, SCHNEEBERGER D M. Transitional morphology in West Deuteronilus Mensae, Mars: implications for modification of the lowland/upland boundary[J]. Icarus, 1989, 82(1): 111-145 doi: 10.1016/0019-1035(89)90027-4 [131] PARKER T J, GORSLINE D S, SAUNDERS R S, et al. Coastal geomorphology of the Martian northern plains[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 1993, 98(E6): 11061-11078 doi: 10.1029/93JE00618 [132] RODRIGUEZ J A P, FAIRÉN A G, TANAKA K L, et al. Tsunami waves extensively resurfaced the shorelines of an early Martian ocean[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 25106 doi: 10.1038/srep25106 [133] COSTARD F, SÉJOURNÉ A, KELFOUN K, et al. Modeling tsunami propagation and the emplacement of thumbprint terrain in an early Mars ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2017, 122(3): 633-649 doi: 10.1002/2016JE005230 [134] DI ACHILLE G, HYNEK B M. Ancient ocean on Mars supported by global distribution of deltas and valleys[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(7): 459-463 doi: 10.1038/ngeo891 [135] DURAN S, COULTHARD T J, BAYNES E R C. Knickpoints in Martian channels indicate past ocean levels[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 15153 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51574-2 [136] CARR M H, HEAD III J W. Oceans on Mars: an assessment of the observational evidence and possible fate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2003, 108(E5): 5042 [137] XIAO L, HUANG J, KUSKY T, et al. Evidence for marine sedimentary rocks in Utopia Planitia: Zhurong rover observations[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(9): nwad137 doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwad137 [138] TUNG H H, PAUL E L, MIDLER M, et al. Crystallization of Organic Compounds[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 2009 [139] RENNÓ N O, BOS B J, CATLING D, et al. Possible physical and thermodynamical evidence for liquid water at the Phoenix landing site[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E1): E00E03 [140] JONES E G. Shallow transient liquid water environments on present-day mars, and their implications for life[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 146: 144-150 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.02.027 [141] MARTÍN-TORRES F J, ZORZANO M P, VALENTÍN-SERRANO P, et al. Transient liquid water and water activity at Gale crater on Mars[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(5): 357-361 doi: 10.1038/ngeo2412 [142] GLAVIN D P, FREISSINET C, MILLER K E, et al. Evidence for perchlorates and the origin of chlorinated hydrocarbons detected by SAM at the Rocknest aeolian deposit in Gale Crater[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2013, 118(10): 1955-1973 doi: 10.1002/jgre.20144 [143] MARTÍNEZ G M, FISCHER E, RENNÓ N O, et al. Likely frost events at Gale crater: analysis from MSL/REMS measurements[J]. Icarus, 2016, 280: 93-102 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2015.12.004 [144] LAURO S E, PETTINELLI E, CAPRARELLI G, et al. Multiple subglacial water bodies below the south pole of Mars unveiled by new MARSIS data[J]. Nature Astronomy, 2021, 5(1): 63-70 [145] OROSEI R, LAURO S E, PETTINELLI E, et al. Radar evidence of subglacial liquid water on Mars[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6401): 490-493 doi: 10.1126/science.aar7268 [146] SCHMIDT F, WAY M J, COSTARD F, et al. Circumpolar ocean stability on Mars 3 Gy ago[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2022, 119(4): e2112930118 [147] NIXON S L, COUSINS C R, COCKELL C S. Plausible microbial metabolisms on Mars[J]. Astronomy :Times New Roman;">& Geophysics, 2013, 54(1): 1.13-1.16 [148] STRAUB K L, BENZ M, SCHINK B, et al. Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent microbial oxidation of ferrous iron[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(4): 1458-1460 doi: 10.1128/aem.62.4.1458-1460.1996 [149] LOVLEY D R, GIOVANNONI S J, WHITE D C, et al. Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov. , a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 1993, 159(4): 336-344 [150] COLEMAN M L, HEDRICK D B, LOVLEY D R, et al. Reduction of Fe (III) in sediments by sulphate-reducing bacteria[J]. Nature, 1993, 361(6411): 436-438 doi: 10.1038/361436a0 [151] WEBER K A, ACHENBACH L A, COATES J D. Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2006, 4(10): 752-764 doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1490 [152] CLARK B C. Solar-driven chemical energy source for a Martian biota[J]. Origins of Life, 1979, 9(3): 241-249 doi: 10.1007/BF00932498 [153] INMAN R E, INGERSOLL R B, LEVY E A. Soil: a natural sink for carbon monoxide[J]. Science, 1971, 172(3989): 1229-1231 doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1229 [154] DANIELS L, FUCHS G, THAUER R K, et al. Carbon monoxide oxidation by methanogenic bacteria[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1977, 132(1): 118-126 doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.118-126.1977 [155] RAMKISSOON N K, TURNER S M R, MACEY M C, et al. Exploring the environments of Martian impact‐generated hydrothermal systems and their potential to support life[J]. Meteoritics :Times New Roman;">& Planetary Science, 2021, 56(7): 1350-1368 [156] OJHA L, KARUNATILLAKE S, KARIMI S, et al. Amagmatic hydrothermal systems on Mars from radiogenic heat[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1754 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21762-8 [157] DUHAMEL S, HAMILTON C W, PÁLSSON S, et al. Microbial response to increased temperatures within a lava-induced hydrothermal system in Iceland: an analogue for the habitability of volcanic terrains on Mars[J]. Astrobiology, 2022, 22(10): 1176-1198 doi: 10.1089/ast.2021.0124 [158] ABRAMOV O, KRING D A. Impact-induced hydrothermal activity on early Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2005, 110(E12): E12S09 [159] COSTELLO L J, FILIBERTO J, CRANDALL J R, et al. Habitability of hydrothermal systems at Jezero and Gusev Craters as constrained by hydrothermal alteration of a terrestrial mafic dike[J]. Geochemistry, 2020, 80(2): 125613 doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125613 [160] EHLMANN B L, MUSTARD J F, CLARK R N, et al. Evidence for low-grade metamorphism, hydrothermal alteration, and diagenesis on Mars from phyllosilicate mineral assemblages[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2011, 59(4): 359-377 doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590402 [161] RAMIREZ R M, CRADDOCK R A. The geological and climatological case for a warmer and wetter early Mars[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(4): 230-237 doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0093-9 [162] CHEVRIER V, POULET F, BIBRING J P. Early geochemical environment of Mars as determined from thermodynamics of phyllosilicates[J]. Nature, 2007, 448(7149): 60-63 doi: 10.1038/nature05961 [163] PALUMBO A M, HEAD J W, WILSON L. Rainfall on Noachian Mars: nature, timing, and influence on geologic processes and climate history[J]. Icarus, 2020, 347: 113782 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2020.113782 [164] RAMIREZ R M, KOPPARAPU R, ZUGGER M E, et al. Warming early Mars with CO2 and H2[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7(1): 59-63 doi: 10.1038/ngeo2000 [165] CHASSEFIÈRE E, LANGLAIS B, QUESNEL Y, et al. The fate of early Mars’ lost water: the role of serpentinization[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2013, 118(5): 1123-1134 doi: 10.1002/jgre.20089 [166] REDD N T. Early Mars may have boasted a large ocean and cool climate[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(50): 31558-31560 [167] MALIN M C, EDGETT K S. Evidence for persistent flow and aqueous sedimentation on early Mars[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5652): 1931-1934 doi: 10.1126/science.1090544 [168] RAMIREZ R M, CRADDOCK R A, USUI T. Climate simulations of early Mars with estimated precipitation, runoff, and erosion rates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2020, 125(3): e2019JE006160 doi: 10.1029/2019JE006160 [169] KAMADA A, KURODA T, KASABA Y, et al. A coupled atmosphere–hydrosphere global climate model of early Mars: a “cool and wet” scenario for the formation of water channels[J]. Icarus, 2020, 338: 113567 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2019.113567 [170] HOU Z Q, LIU J Z, XU Y G, et al. The search for life signatures on Mars by the Tianwen-3 Mars sample return mission[J]. National Science Review, 2024, 11(11): nwae313 doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae313 [171] LOIZEAU D, WERNER S C, MANGOLD N, et al. Chronology of deposition and alteration in the Mawrth Vallis region, Mars[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2012, 72(1): 31-43 doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2012.06.023 [172] WRIGHT J, BALME M, DAVIS J, et al. Geological mapping of Mawrth Vallis, Mars, by PLANMAP[C]//14th Europlanet Science Congress 2020. Virtual Meeting (Online): Europlanet Society, 2020 [173] LOIZEAU D, MANGOLD N, POULET F, et al. Phyllosilicates in the Mawrth Vallis region of Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2007, 112(E8): E08S08 [174] MICHALSKI J R, BIBRING J P, POULET F, et al. The Mawrth Vallis region of Mars: a potential landing site for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission[J]. Astrobiology, 2010, 10(7): 687-703 doi: 10.1089/ast.2010.0491 [175] WRAY J J, EHLMANN B L, SQUYRES S W, et al. Compositional stratigraphy of clay-bearing layered deposits at Mawrth Vallis, Mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(12): L12202 [176] FARRAND W H, GLOTCH T D, HORGAN B. Detection of copiapite in the northern Mawrth Vallis region of Mars: evidence of acid sulfate alteration[J]. Icarus, 2014, 241: 346-357 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2014.07.003 [177] BISHOP J L, GROSS C, DANIELSEN J, et al. Multiple mineral horizons in layered outcrops at Mawrth Vallis, Mars, signify changing geochemical environments on early Mars[J]. Icarus, 2020, 341: 113634 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2020.113634 [178] Geologic Map of Mars . (2014-07-14)[2025-3-5]. https://pubs.usgs.gov/sim/3292/. [179] MCKEOWN N K, BISHOP J L, NOE DOBREA E Z, et al. Characterization of phyllosilicates observed in the central Mawrth Vallis region, Mars, their potential formational processes, and implications for past climate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E2): E00D10 [180] LOIZEAU D, MANGOLD N, POULET F, et al. Stratigraphy in the Mawrth Vallis region through OMEGA, HRSC color imagery and DTM[J]. Icarus, 2010, 205(2): 396-418 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2009.04.018 [181] MICHALSKI J R, CUADROS J, NILES P B, et al. Groundwater activity on Mars and implications for a deep biosphere[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(2): 133-138 doi: 10.1038/ngeo1706 [182] MICHALSKI J R, GLOTCH T D, ROGERS A D, et al. The geology and astrobiology of McLaughlin crater, Mars: an ancient lacustrine basin containing turbidites, mudstones, and serpentinites[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2019, 124(4): 910-940 doi: 10.1029/2018JE005796 [183] GARY-BICAS C E, ROGERS A D. Geologic and thermal characterization of Oxia Planum using Mars Odyssey THEMIS data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2021, 126(2): e2020JE006678 doi: 10.1029/2020JE006678 [184] FAWDON P, ORGEL C, ADELI S, et al. The high-resolution map of Oxia Planum, Mars; the landing site of the ExoMars Rosalind Franklin rover mission[J]. Journal of Maps, 2024, 20(1): 2302361 doi: 10.1080/17445647.2024.2302361 [185] KRZESIŃSKA A M, BULTEL B, LOIZEAU D, et al. Mineralogical and spectral (near-infrared) characterization of Fe-rich vermiculite-bearing terrestrial deposits and constraints for mineralogy of Oxia Planum, ExoMars 2022 landing site[J]. Astrobiology, 2021, 21(8): 997-1016 doi: 10.1089/ast.2020.2410 [186] PAN L, CARTER J, QUANTIN-NATAF C, et al. Voluminous silica precipitated from Martian waters during late-stage aqueous alteration[J]. The Planetary Science Journal, 2021, 2(2): 65 doi: 10.3847/PSJ/abe541 [187] QUANTIN-NATAF C, CARTER J, MANDON L, et al. Oxia Planum: the landing site for the ExoMars “Rosalind Franklin” rover mission: geological context and prelanding interpretation[J]. Astrobiology, 2021, 21(3): 345-366 doi: 10.1089/ast.2019.2191 [188] MCNEIL J D, FAWDON P, BALME M R, et al. Mounds in Oxia Planum: the burial and exhumation of the ExoMars rover landing site[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2022, 127(11): e2022JE007246 doi: 10.1029/2022JE007246 [189] RUIZ-GALENDE P, FERNÁNDEZ G, TORRE-FDEZ I, et al. Characterization of sedimentary and volcanic rocks in Armintza outcrop (Biscay, Spain) and its implication for Oxia Planum (Mars) exploration[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2021, 251: 119443 doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119443 [190] ZHAO J N, XIAO Z J, HUANG J, et al. Geological characteristics and targets of high scientific interest in the Zhurong landing region on Mars[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(20): e2021GL094903 doi: 10.1029/2021GL094903 [191] THOMSON B J, HEAD III J W. Utopia Basin, Mars: characterization of topography and morphology and assessment of the origin and evolution of basin internal structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2001, 106(E10): 23209-23230 doi: 10.1029/2000JE001355 [192] MORGENSTERN A, HAUBER E, REISS D, et al. Deposition and degradation of a volatile‐rich layer in Utopia Planitia and implications for climate history on Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2007, 112(E6): E06010 [193] IVANOV M A, HIESINGER H, ERKELING G, et al. Mud volcanism and morphology of impact craters in Utopia Planitia on Mars: evidence for the ancient ocean[J]. Icarus, 2014, 228: 121-140 doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2013.09.018 [194] LIU Y, WU X, ZHAO Y Y S, et al. Zhurong reveals recent aqueous activities in Utopia Planitia, Mars[J]. Science Advances, 2022, 8(19): eabn8555 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn8555 [195] KRESLAVSKY M A, HEAD J W. Fate of outflow channel effluents in the northern lowlands of Mars: the Vastitas Borealis Formation as a sublimation residue from frozen ponded bodies of water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2002, 107(E12): 4 [196] WANG L, ZHAO J N, HUANG J, et al. An explosive mud volcano origin for the pitted cones in southern Utopia Planitia, Mars[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2023, 66(9): 2045-2056 doi: 10.1007/s11430-022-1119-1 [197] CLIFFORD S M, PARKER T J. The evolution of the Martian hydrosphere: implications for the fate of a primordial ocean and the current state of the northern plains[J]. Icarus, 2001, 154(1): 40-79 doi: 10.1006/icar.2001.6671 [198] WU B, DONG J, WANG Y R, et al. Landing site selection and characterization of Tianwen‐1 (Zhurong Rover) on Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2022, 127(4): e2021JE007137 doi: 10.1029/2021JE007137 -
-





 万李明 女, 2000年2月出生于河南省开封市, 现为中国科学院地球化学研究所月球与行星科学中心硕士研究生, 主要从事火星遥感地貌水环境相关的研究. E-mail:
万李明 女, 2000年2月出生于河南省开封市, 现为中国科学院地球化学研究所月球与行星科学中心硕士研究生, 主要从事火星遥感地貌水环境相关的研究. E-mail: 

 下载:
下载: