Comparison of Geomagnetic Models with Different Spatio-temporal Resolutions and Measured Data from Geomagnetic Stations
-
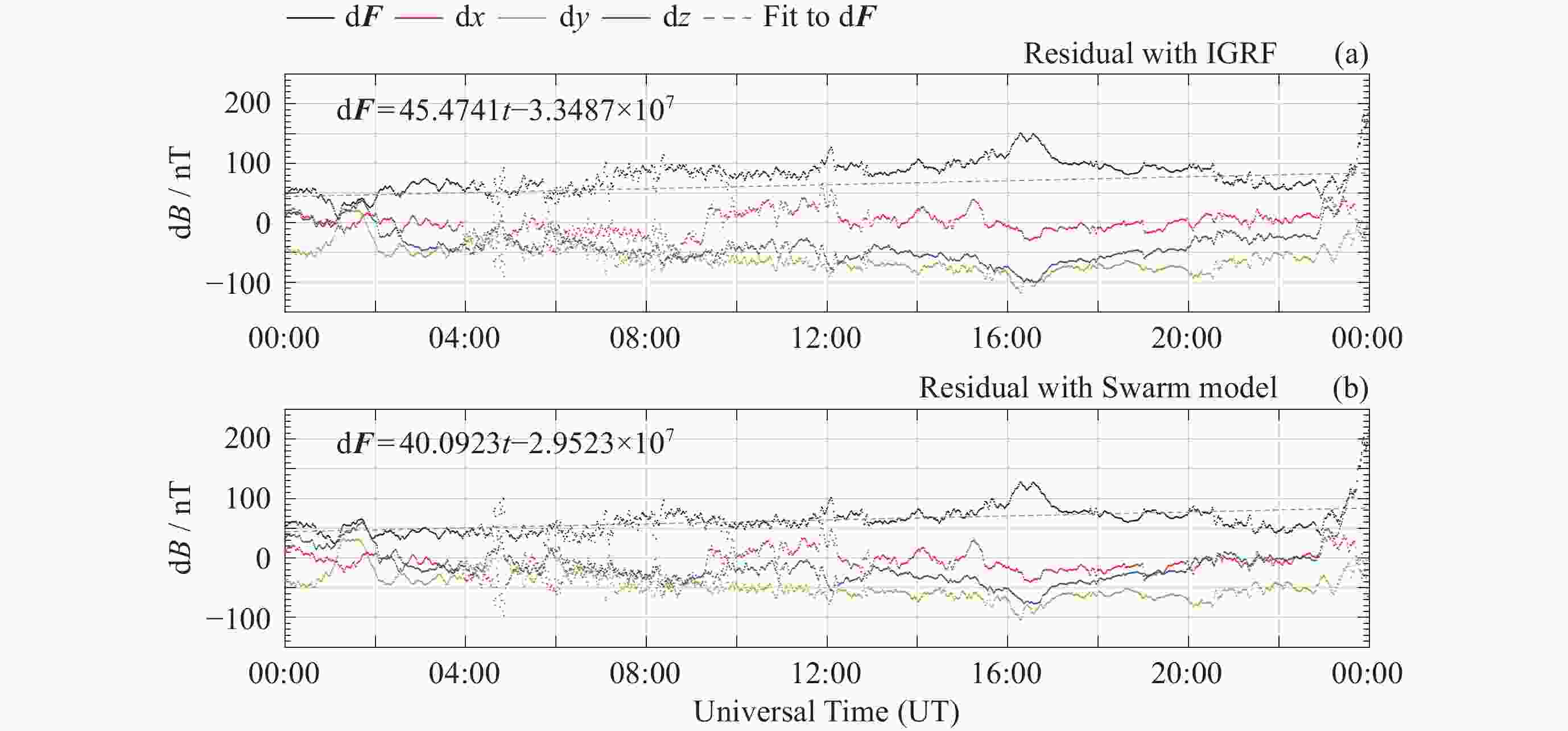
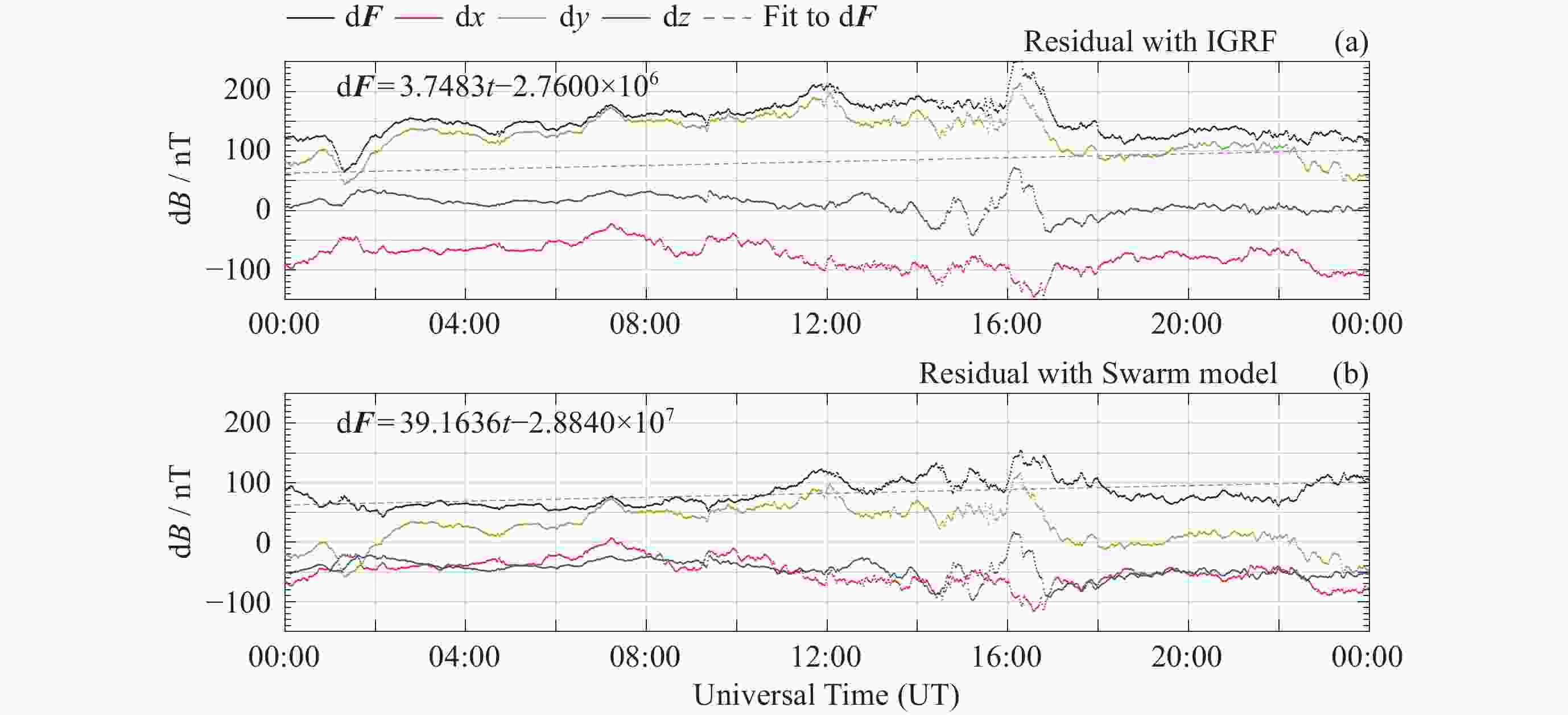
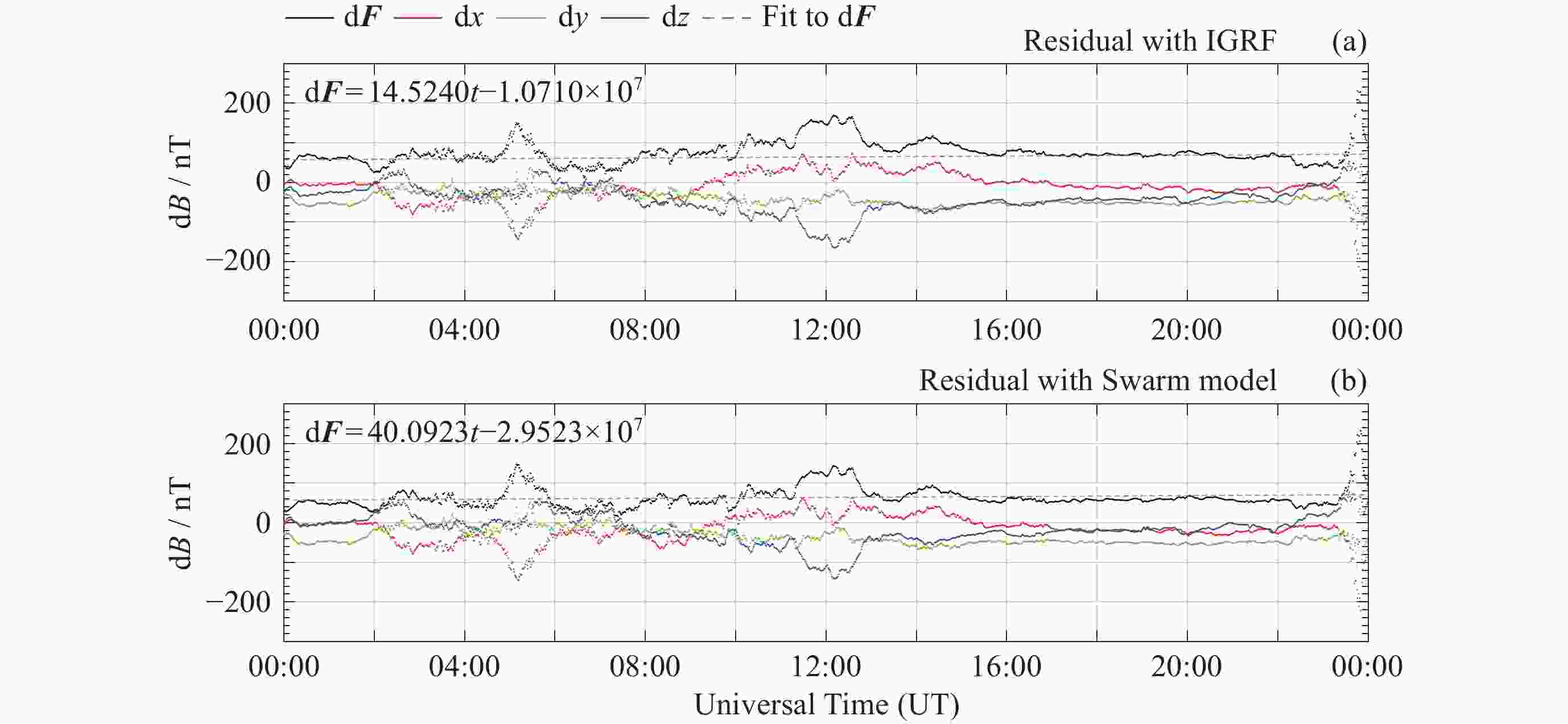
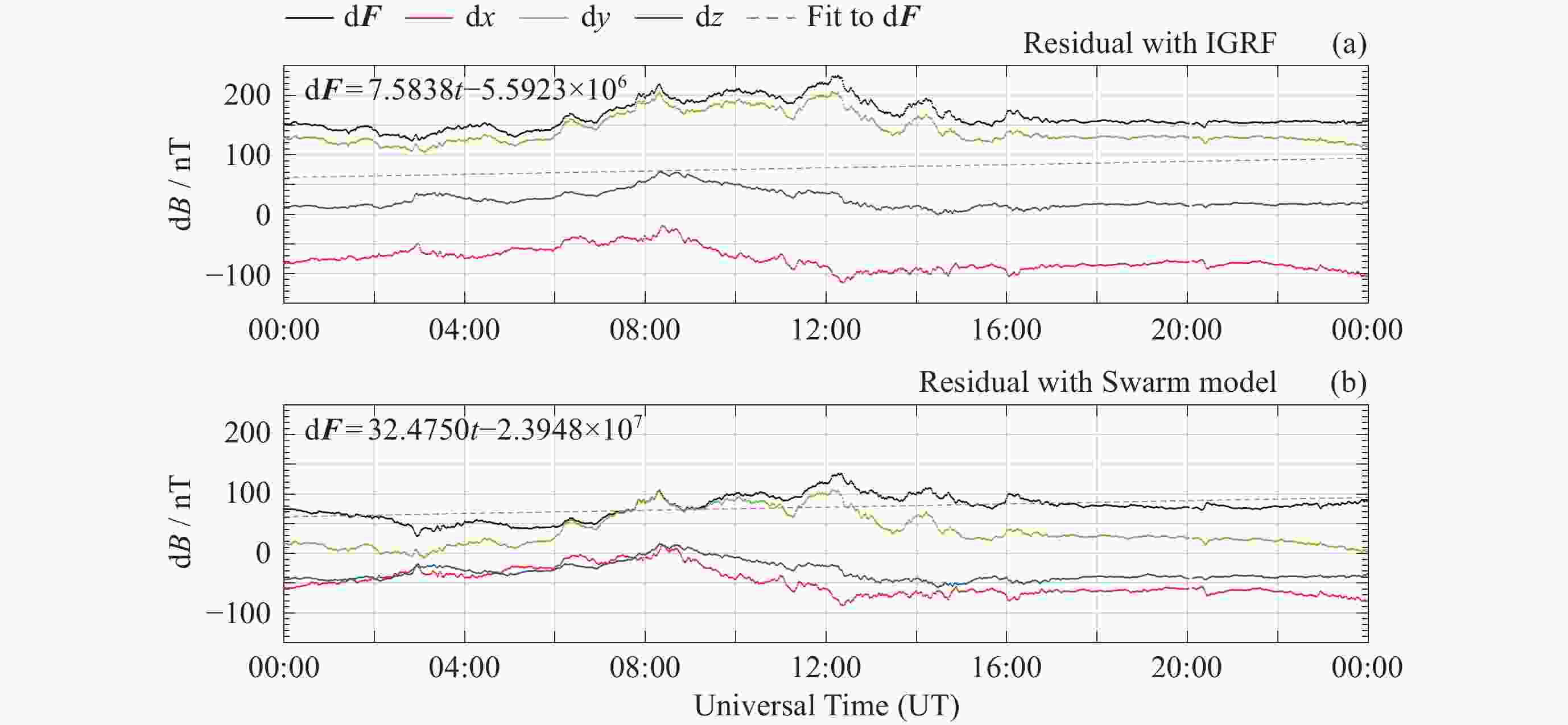
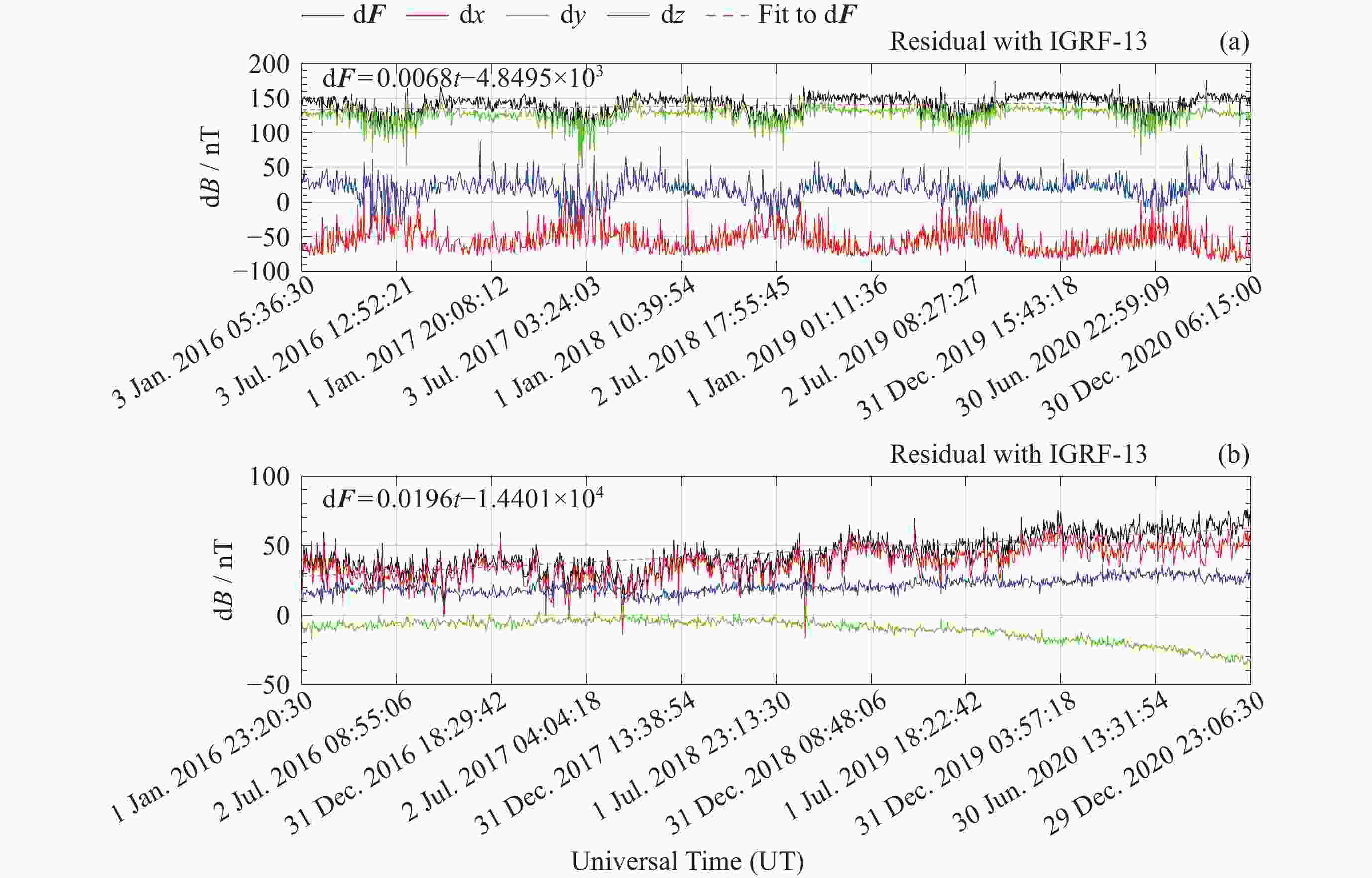
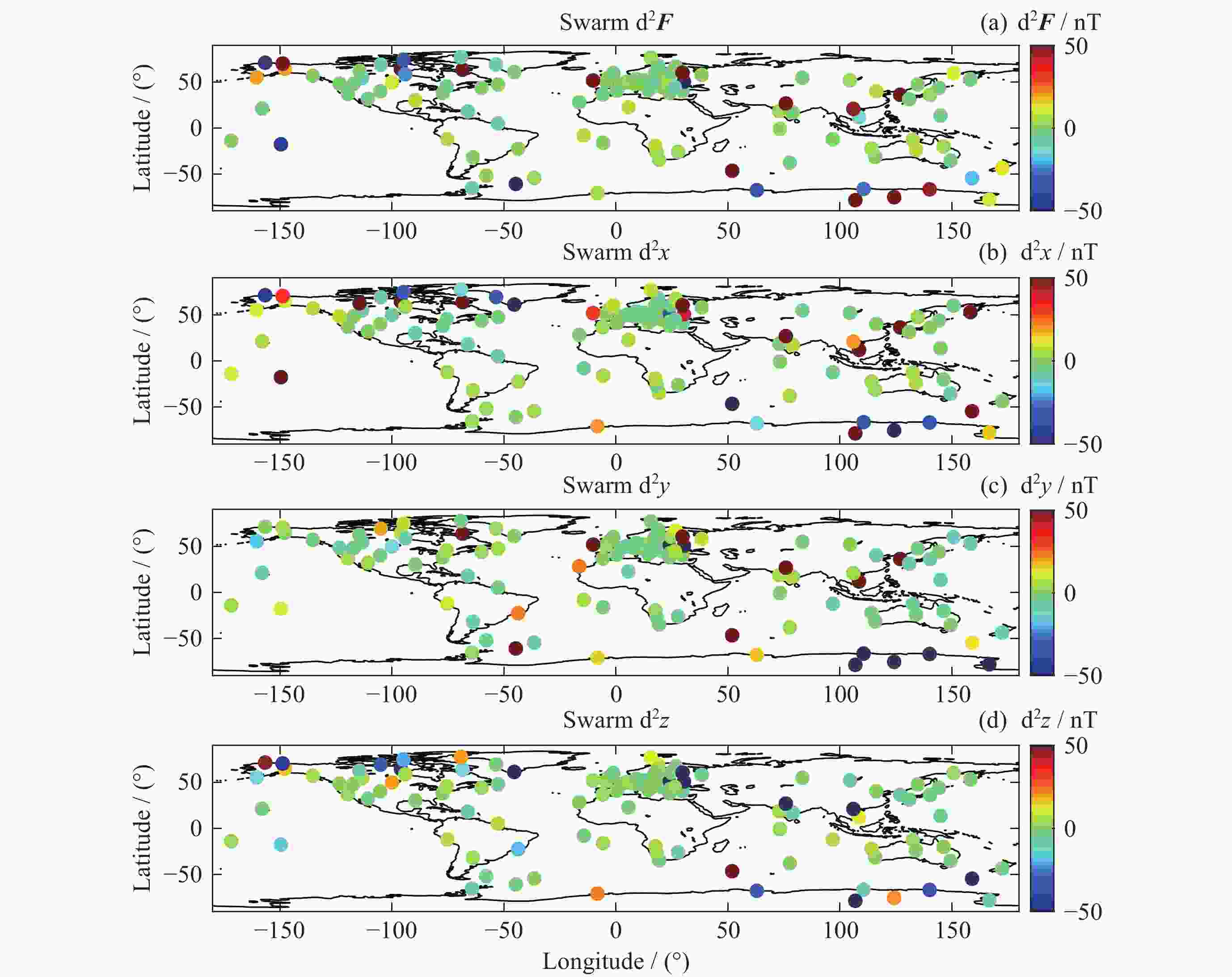
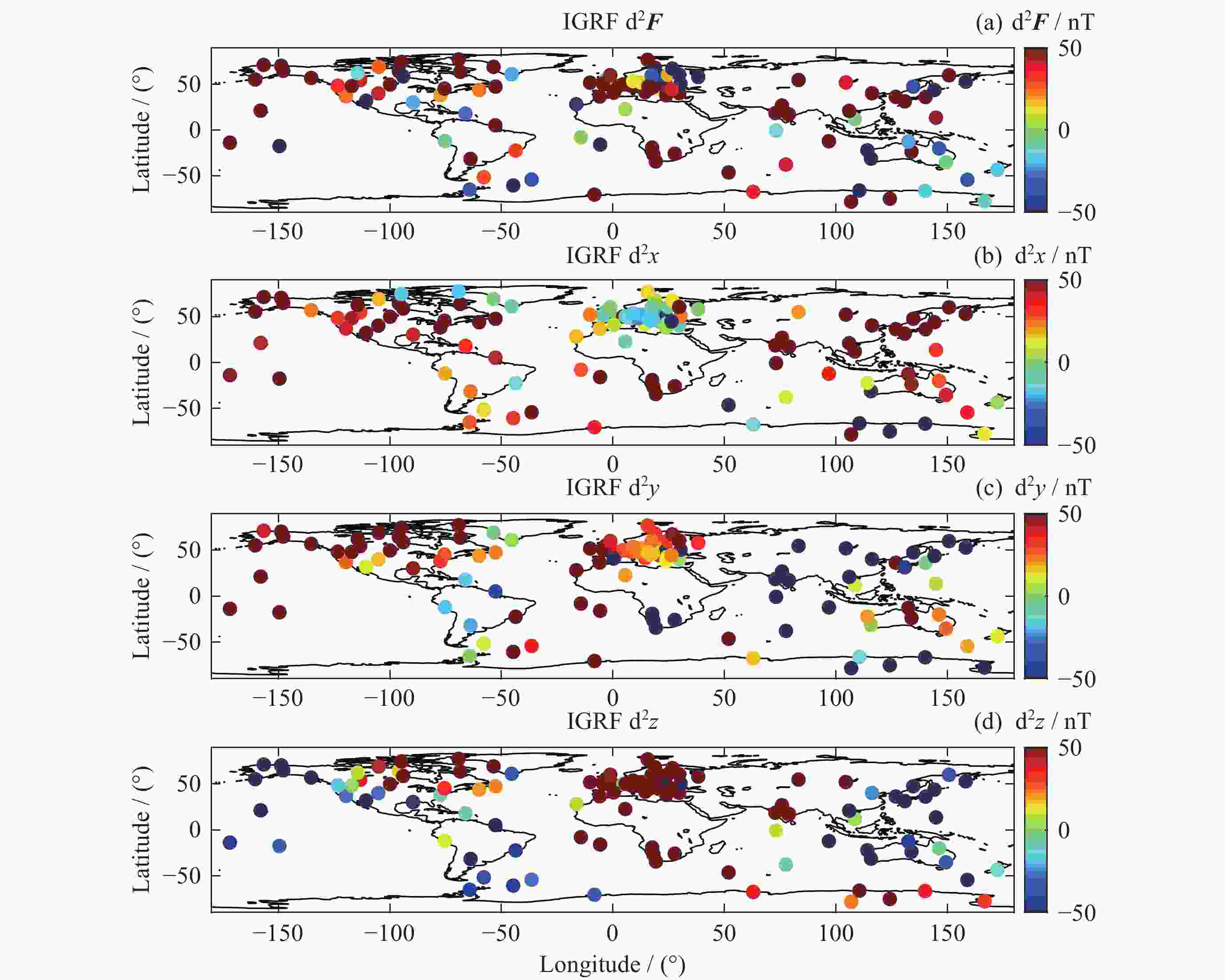
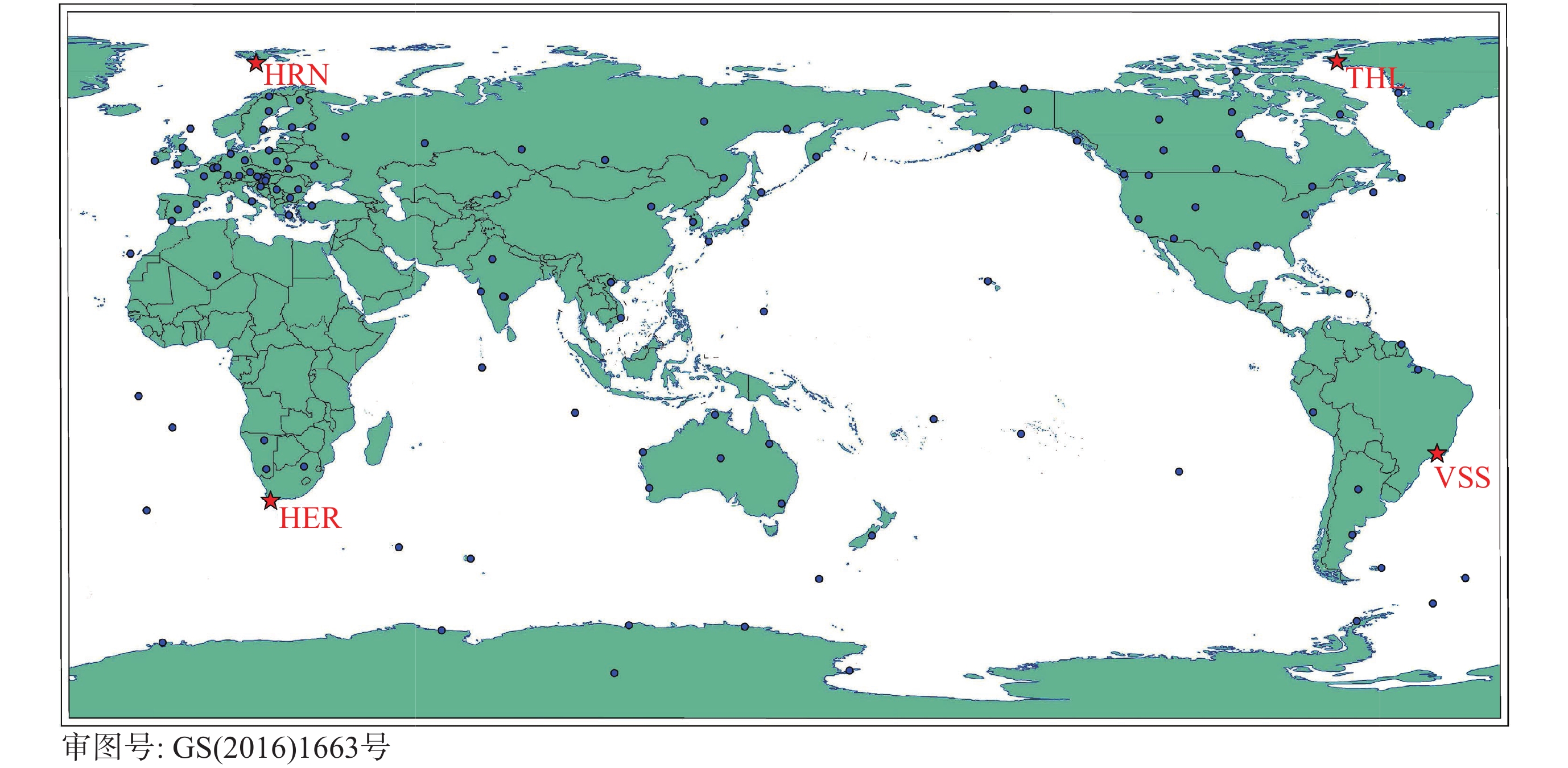
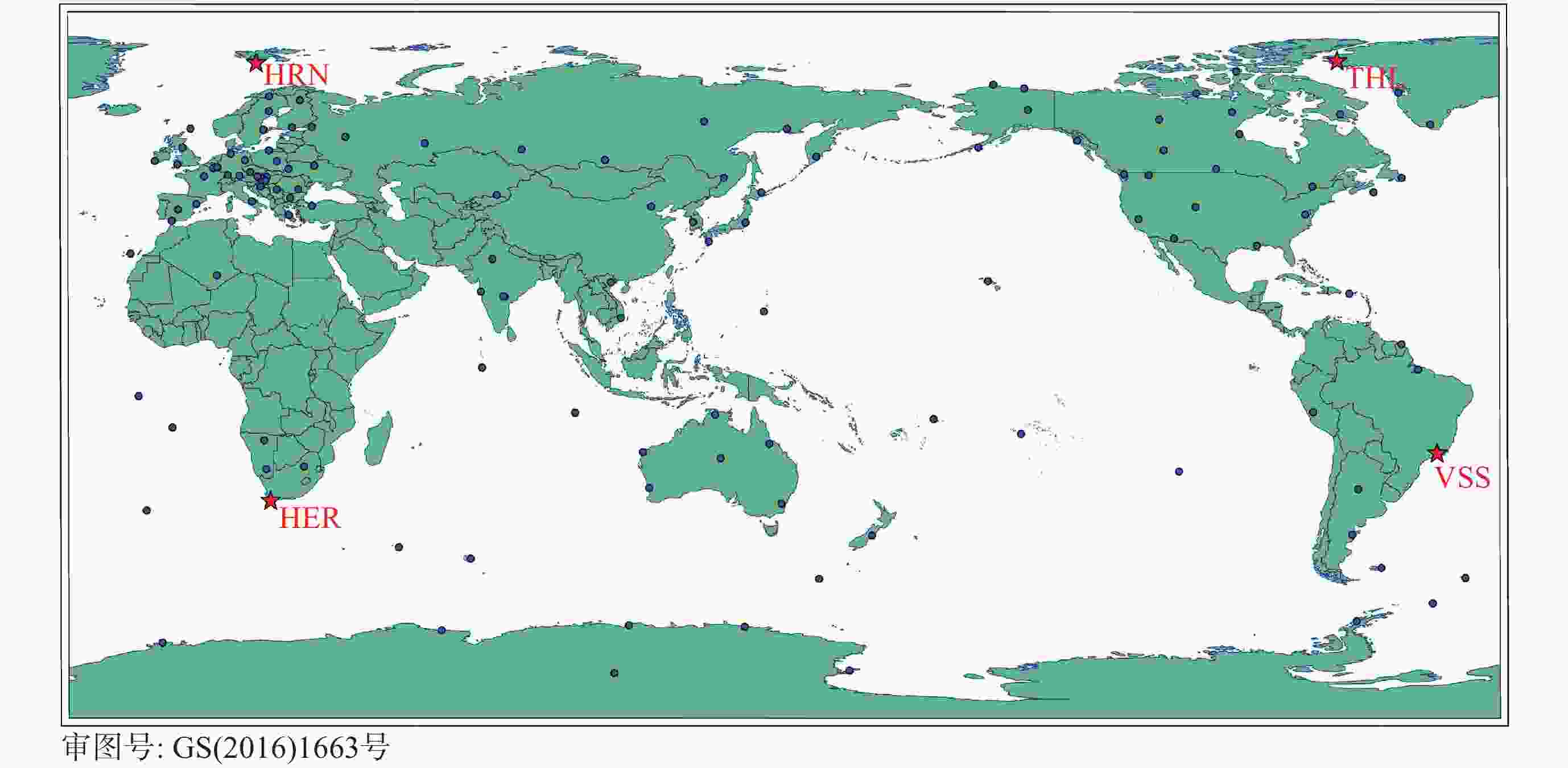
摘要: 在近年来磁场变化较快的北极以及南大西洋异常区选取了国际地磁台网(INTERMAGNET)的4个地磁台站, 利用国际地磁参考场模型IGRF以及目前国内时空分辨率最高的多场源Swarm模型两个时空分辨率不同的全球地磁场模型, 定量研究了模型空间分辨率以及更新周期相对地磁台站实测数据的偏差. 研究结果表明: 同等更新周期情况下, 在太阳活动宁静时期, 对于岩石圈磁异常不明显的区域, IGRF和其他空间分辨率更高的地磁场模型给出的结果较为接近, 而对于岩石圈磁异常较为明显的区域, 空间分辨率更高的全球地磁场模型更接近实测值; 在IGRF未更新的5年 (2016-2020年)内, 地磁台站实测值与IGRF模型之间存在明显的时间漂移, 典型漂移可达100 nT以上, 但漂移的量值也存在地区差异, 这与地磁场全球变化不均匀有关. 相比之下, 地磁台站观测值与Swarm模型之间则未观测到明显的漂移现象. 这一结果表明, 在地磁场快速变化时期, 缩短主磁场的更新周期十分必要. 本项研究可以为全球地磁场模型的相关应用提供依据和参考.Abstract: This study focuses on four INTERMAGNET geomagnetic stations located in the Arctic region and the South Atlantic Anomaly regions, where rapid geomagnetic changes have been observed in recent years. Utilizing two global geomagnetic field models with different spatial and temporal resolutions, the International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) model and the Swarm model, a multi-field source model that offers the highest spatiotemporal resolution currently available in China. The influence of model spatial resolution and update cycles on observatory measurements is quantitatively assessed. The findings are as follows. In regions without significant lithospheric magnetic anomalies, the IGRF and Swarm models yield relatively consistent results. However, for regions with more prominent lithospheric magnetic anomalies, the Swarm model with higher spatial resolution provides better agreement with the measurements. While the IGRF model showed significant temporal drift (often exceeding 100 nT) against station measurements during its five-year non-update period (from 2016 to 2020), the Swarm model exhibited no such drift. The magnitude of the IGRF drift varied regionally, reflecting the heterogeneity of global geomagnetic field variations. These results highlight the need to shorten the update interval for core field models during periods of rapid geomagnetic change. Statistical analysis from 120 global INTERMAGNET (International Real-time Magnetic Observatory Network) stations further confirms that, within the IGRF’s five-year update cycle, the Swarm model exhibits smaller mean and median absolute deviation compared to the IGRF model. The higher spatiotemporal resolution of the Swarm model yields results that are more consistent with observations and thus offers a more accurate representation of the geomagnetic field. This study provides a valuable basis and reference for the application of global geomagnetic models.
-
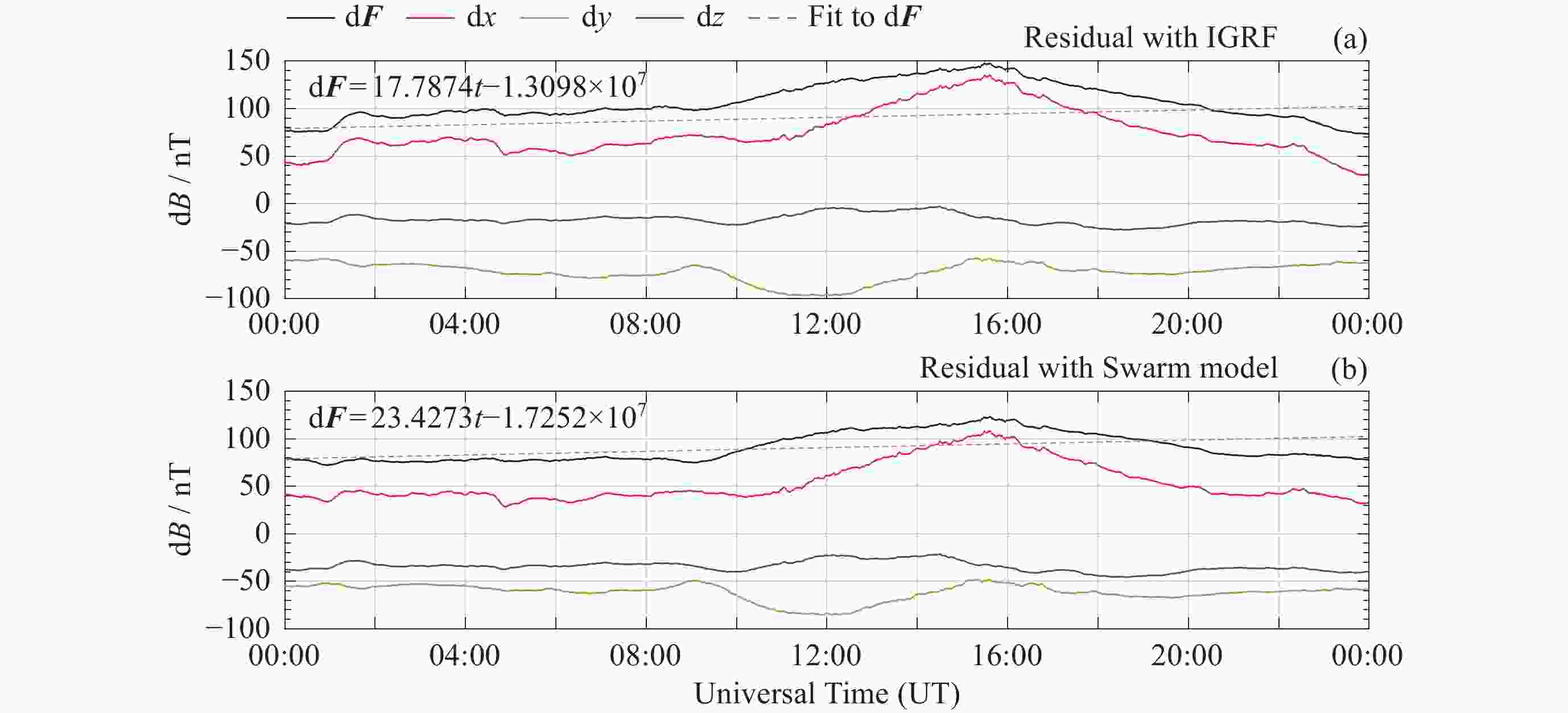
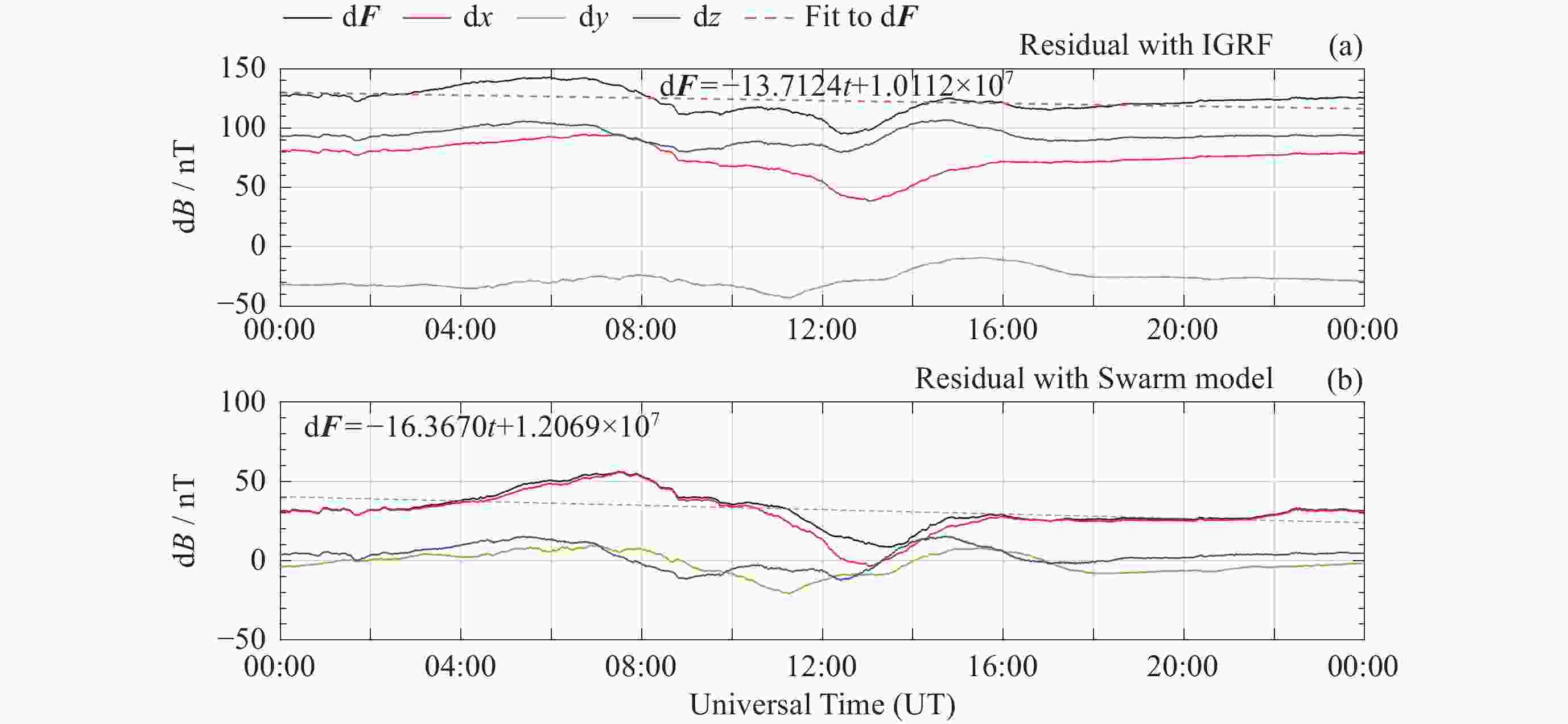
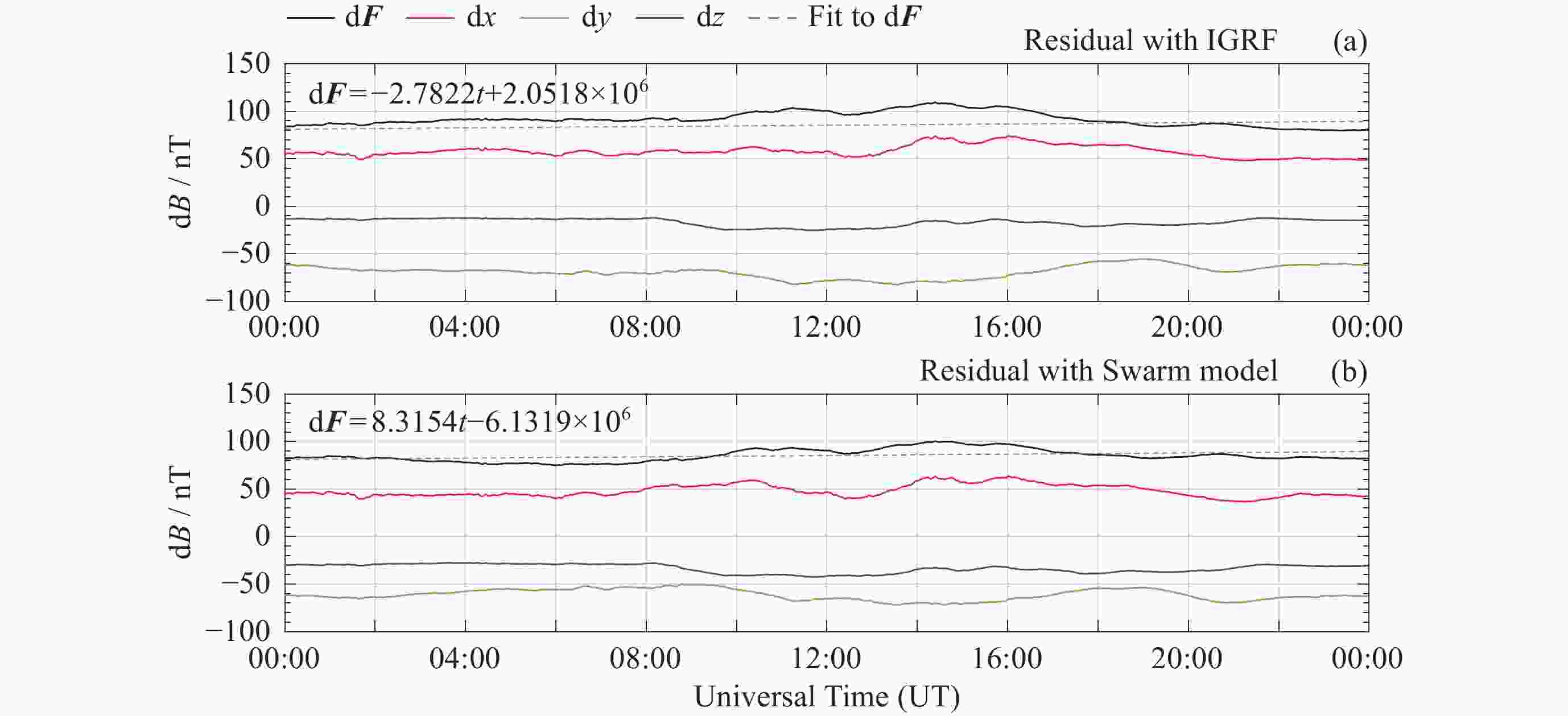
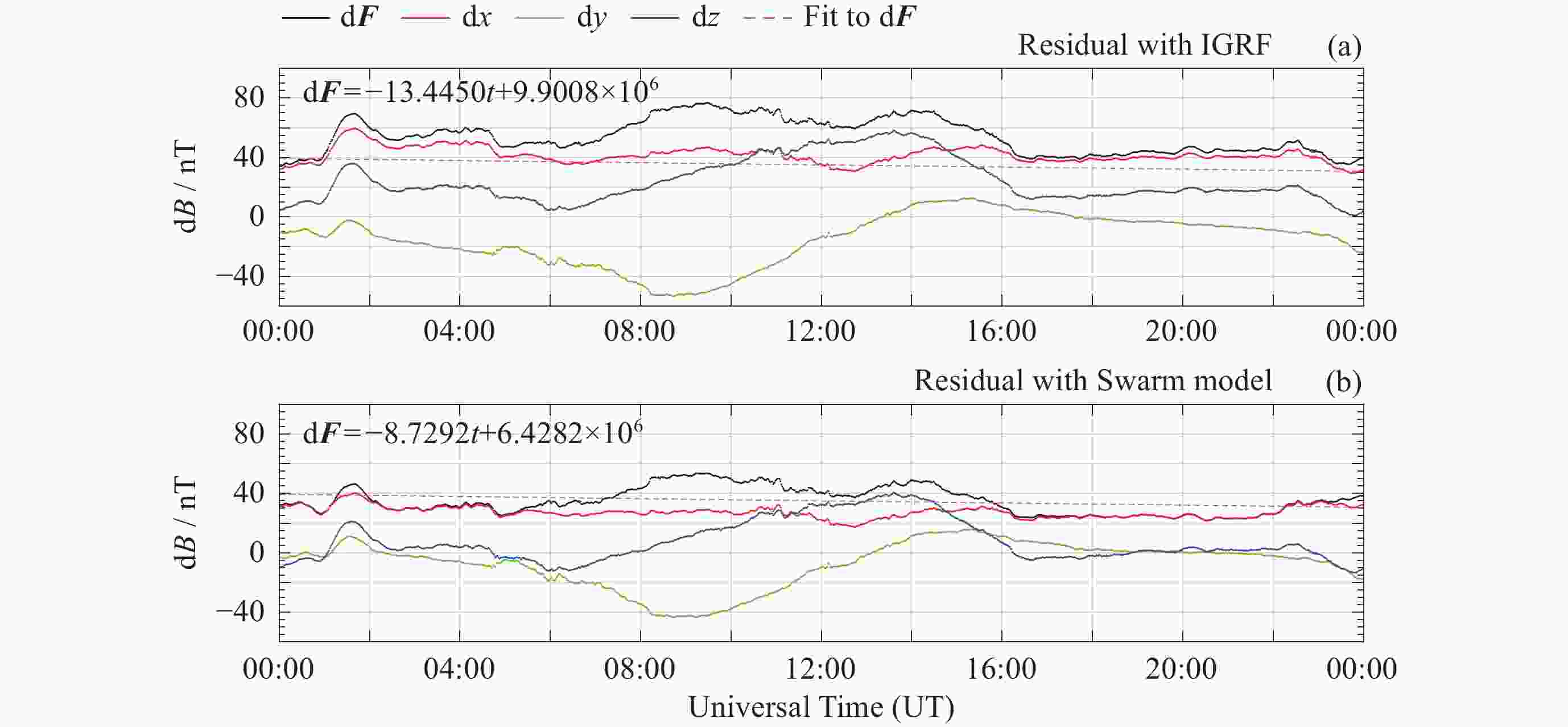
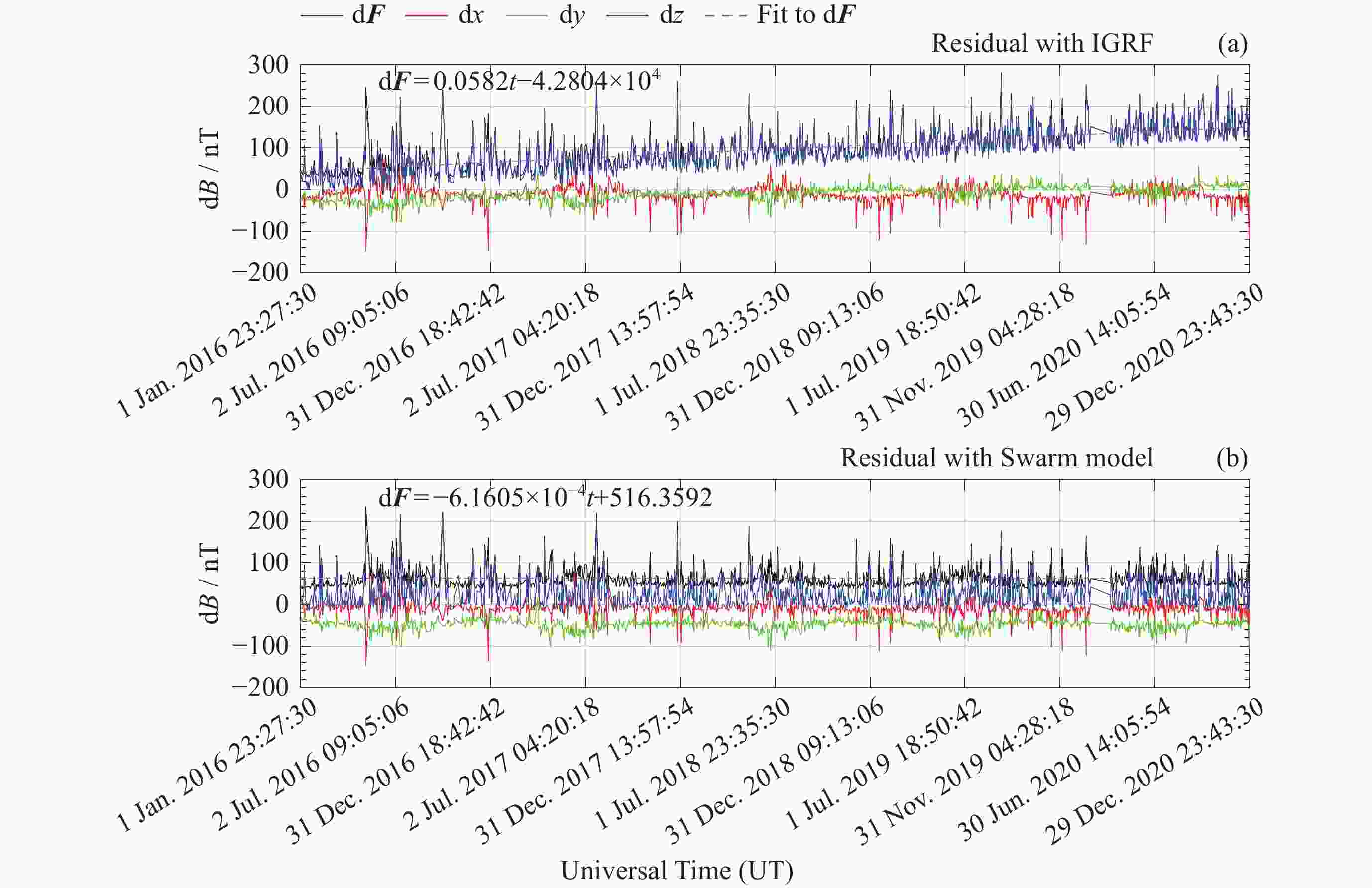
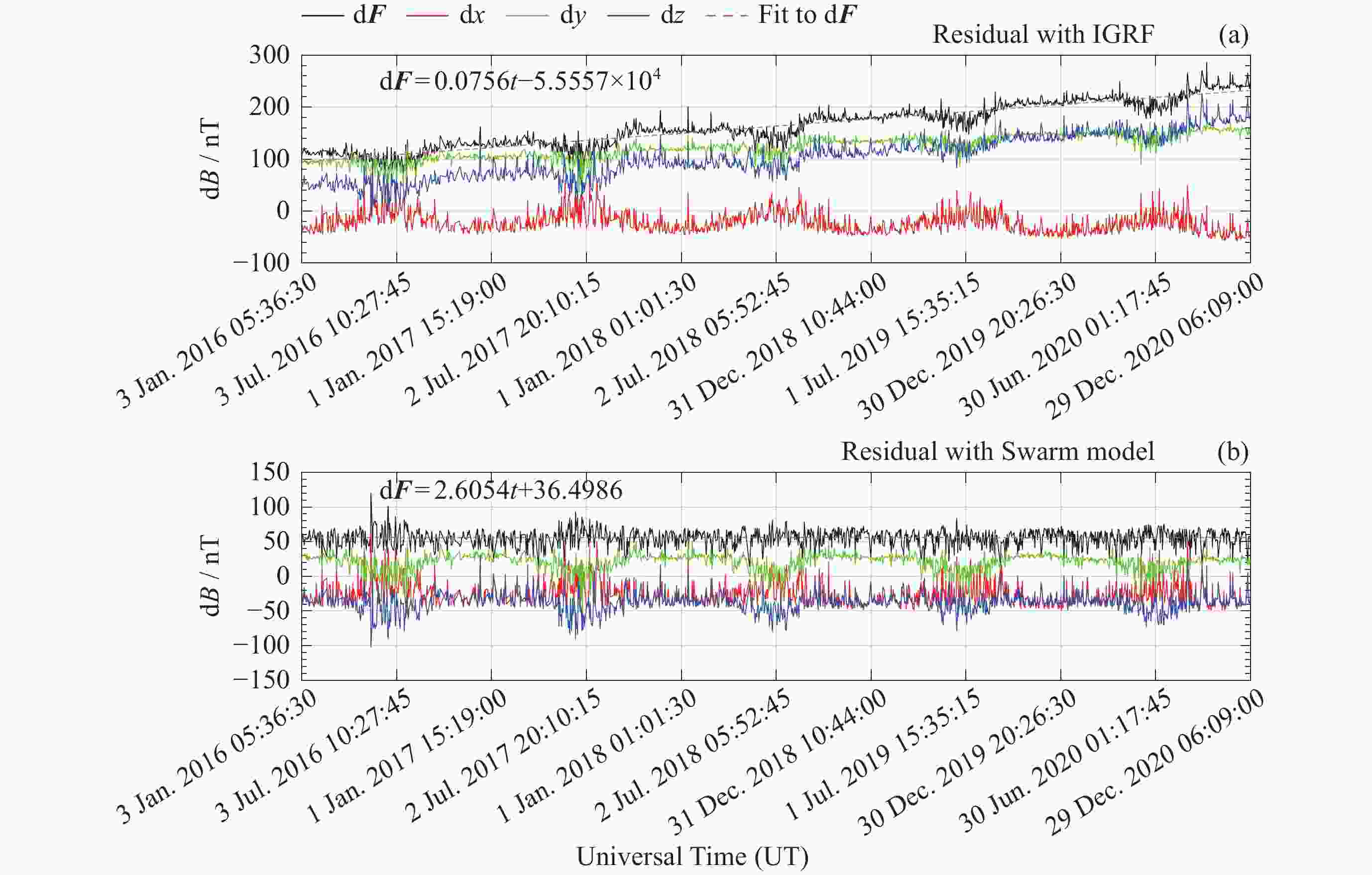
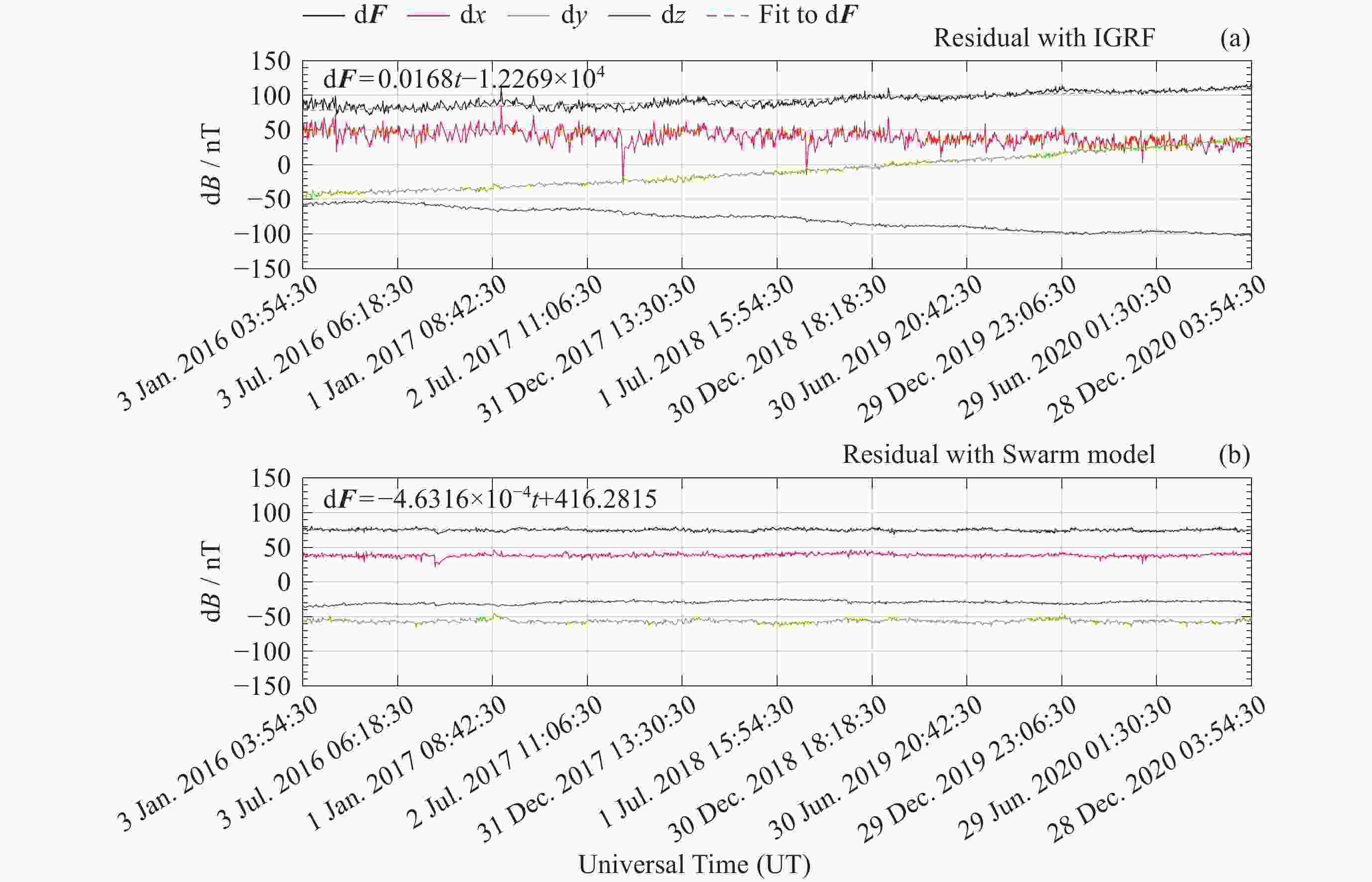
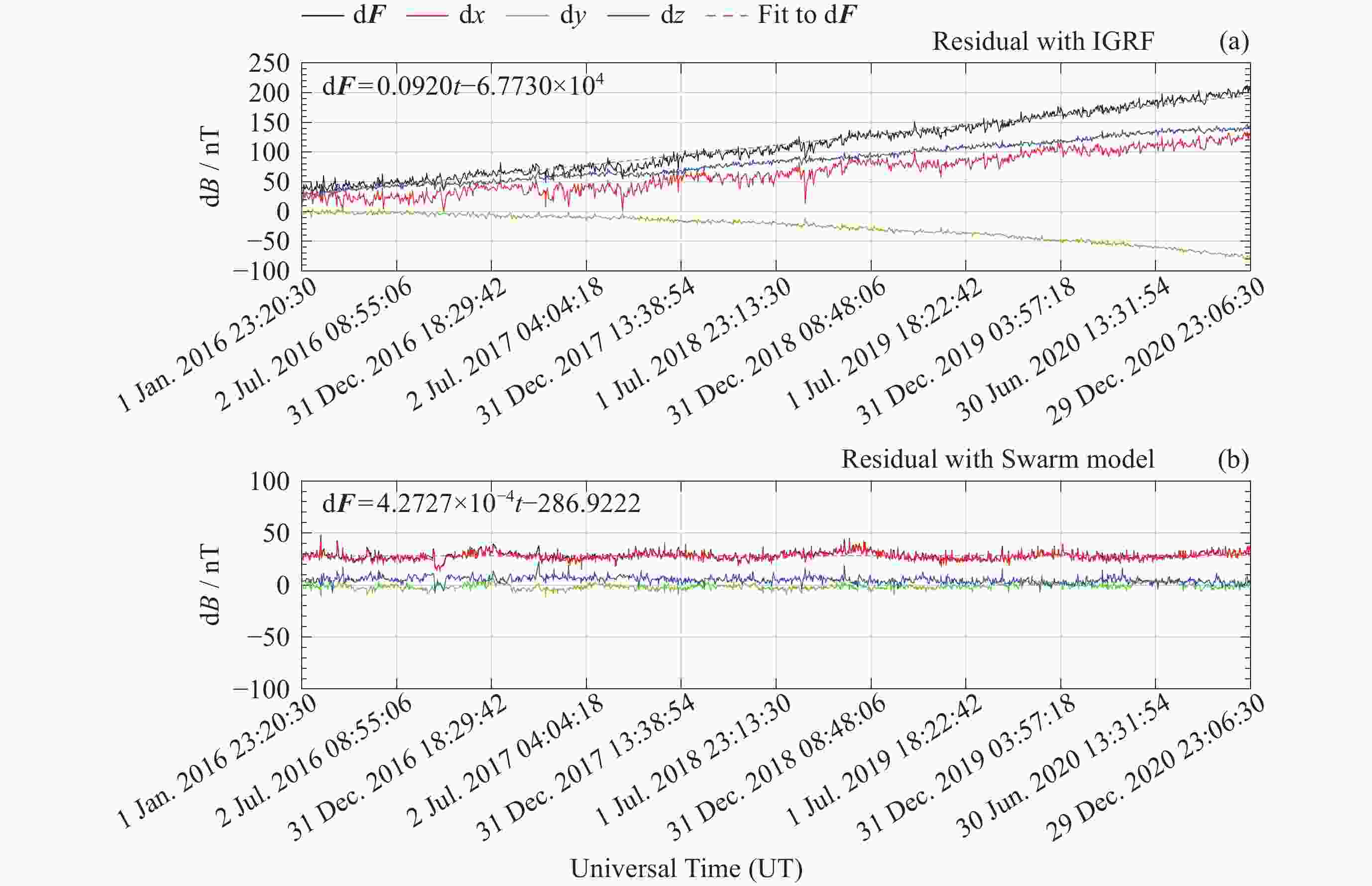
表 1 5年内地磁台站观测值与IGRF模型残差值变化
Table 1. Change of residual values between geomagnetic station observations and IGRF models in five years
台站 d2x/nT d2y/nT d2z/nT d2F/nT $ \dfrac{\mathrm{d}^2{\boldsymbol{F}}}{\mathrm{d}t} $/(nT·a–1) HRN ― ― 122.4437 106.6224 21.3245 THL ― 71.1189 132.8542 137.7824 27.5565 VSS ― 81.3349 –52.7932 30.5422 6.1084 HER 107.5876 –72.2271 113.3895 167.8455 33.5691 注 “―”表示随时间漂移不明显的分量不纳入计算. 表 2 模型与台站观测值差值的均值对比
Table 2. Comparison of mean values of differences between models and station observations
模型 d2F/nT d2x/nT d2y/nT d2z/nT Swarm 55.2609 15.3731 39.9163 –3.8206 IGRF 95.0589 52.9819 52.6998 25.8081 表 3 模型与台站观测值差值的绝对中位差
Table 3. Median absolute deviation between the model and the station observations
模型 d2F/nT d2x/nT d2y/nT d2z/nT Swarm 4.16735 5.2352 4.7719 4.3705 IGRF 60.6932 39.942875 33.2245 68.30735 -
[1] ALKEN P, THÉBAULT E, BEGGAN C D, et al. International geomagnetic reference field: the thirteenth generation[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 73(1): 49 [2] CHULLIAT A, ALKEN P, NAIR M, et al. The US/UK World Magnetic Model for 2020-2025: Technical Report[R]. Boulder: National Centers for Environmental Information, NOAA, 2020 [3] MAUS S, YIN F, LÜHR H, et al. Resolution of direction of oceanic magnetic lineations by the sixth‐generation lithospheric magnetic field model from CHAMP satellite magnetic measurements[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(7): Q07021 [4] OLSEN N, RAVAT D, FINLAY C C, et al. LCS-1: a high-resolution global model of the lithospheric magnetic field derived from CHAMP and Swarm satellite observations[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2017, 211(3): 1461-1477 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx381 [5] THÉBAULT E, HULOT G, LANGLAIS B, et al. A spherical harmonic model of Earth’s lithospheric magnetic field up to degree 1050[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(21): e2021gl095147 doi: 10.1029/2021GL095147 [6] CHULLIAT A, VIGNERON P, HULOT G. First results from the swarm dedicated ionospheric field inversion chain[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2016, 68(1): 104. doi: 10.1186/s40623-016-0481-6 [7] LAUNDAL K M, FINLAY C C, OLSEN N, et al. Solar wind and seasonal influence on ionospheric currents from swarm and champ measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2018, 123(5): 4402-4429 doi: 10.1029/2018JA025387 [8] EGBERT G D, BENNETT A F, FOREMAN M G G. TOPEX/POSEIDON tides estimated using a global inverse model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1994, 99(C12): 821-852 [9] TYLER R H, MAUS S, LÜHR H. Satellite observations of magnetic fields due to ocean tidal flow[J]. Science, 2003, 299(5604): 239-241 doi: 10.1126/science.1078074 [10] LESUR V, WARDINSKI I, HAMOUDI M, et al. The second generation of the GFZ reference internal magnetic model: GRIMM-2[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2010, 62(10): 765-773 doi: 10.5047/eps.2010.07.007 [11] MAUS S, ROTHER M, STOLLE C, et al. Third generation of the Potsdam Magnetic Model of the Earth (POMME)[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(7): Q07008 [12] OLSEN N, LÜHR H, SABAKA T J, et al. CHAOS—a model of the Earth’s magnetic field derived from CHAMP, Ørsted, and SAC-C magnetic satellite data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2006, 166(1): 67-75 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02959.x [13] FINLAY C C, KLOSS C, OLSEN N, et al. The CHAOS-7 geomagnetic field model and observed changes in the South Atlantic Anomaly[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 156 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01252-9 [14] SABAKA T J, TØFFNER-CLAUSEN L, OLSEN N, et al. CM6: a comprehensive geomagnetic field model derived from both CHAMP and Swarm satellite observations[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2020, 72(1): 80 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01210-5 [15] MAUS S, NAIR M C, POEDJONO B, et al. High definition geomagnetic models: a new perspective for improved wellbore positioning[C]//IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition. San Diego, California, USA: SPE, 2012 [16] YANG Y Y, HULOT G, VIGNERON P, et al. The CSES Global Geomagnetic field Model (CGGM): an IGRF-type global geomagnetic field model based on data from the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2021, 73(1): 1-21 doi: 10.1186/s40623-020-01323-x [17] YANG Yanyan, ZEREN Zhima, SHEN Xuhui, et al. Global geomagnetic field modeling based on Swarm Alpha magnetic field measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(5): 1881-1890 (杨艳艳, 泽仁志玛, 申旭辉, 等. 基于Swarm卫星磁测数据的全球多场源地磁场建模[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(5): 1881-1890YANG Yanyan, ZEREN Zhima, SHEN Xuhui, et al. Global geomagnetic field modeling based on Swarm Alpha magnetic field measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(5): 1881-1890 [18] WANG Q, ZHENG C, WU P L, et al. Geomagnetic/inertial navigation integrated matching navigation method[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(11): e11249 doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11249 [19] MAUS S, BARCKHAUSEN U, BERKENBOSCH H, et al. EMAG2: a 2–arc min resolution Earth magnetic anomaly grid compiled from satellite, airborne, and marine magnetic measurements[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2009, 10(8): Q08005 [20] POEDJONO B, BECK N, BUCHANAN A, et al. Improved geomagnetic referencing in the arctic environment[C]//SPE Arctic and Extreme Environments Technical Conference and Exhibition. Moscow, Russia: SPE, 2013 [21] THÉBAULT E, FINLAY C C, BEGGAN C D, et al. International geomagnetic reference field: the 12th generation[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2015, 67(1): 79 doi: 10.1186/s40623-015-0228-9 [22] HULOT G, SABAKA T J, OLSEN N, et al. The Present and Future Geomagnetic Field[M]. Treatise on Geophysics (2nd Edition). Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015, 5: 33-78 -
-




 徐玥 女, 1999年生, 硕士研究生, 主要从事张衡一号卫星磁场数据处理、地震前电离层磁异常扰动信号分析方面的研究. E-mail:
徐玥 女, 1999年生, 硕士研究生, 主要从事张衡一号卫星磁场数据处理、地震前电离层磁异常扰动信号分析方面的研究. E-mail: 
 下载:
下载: